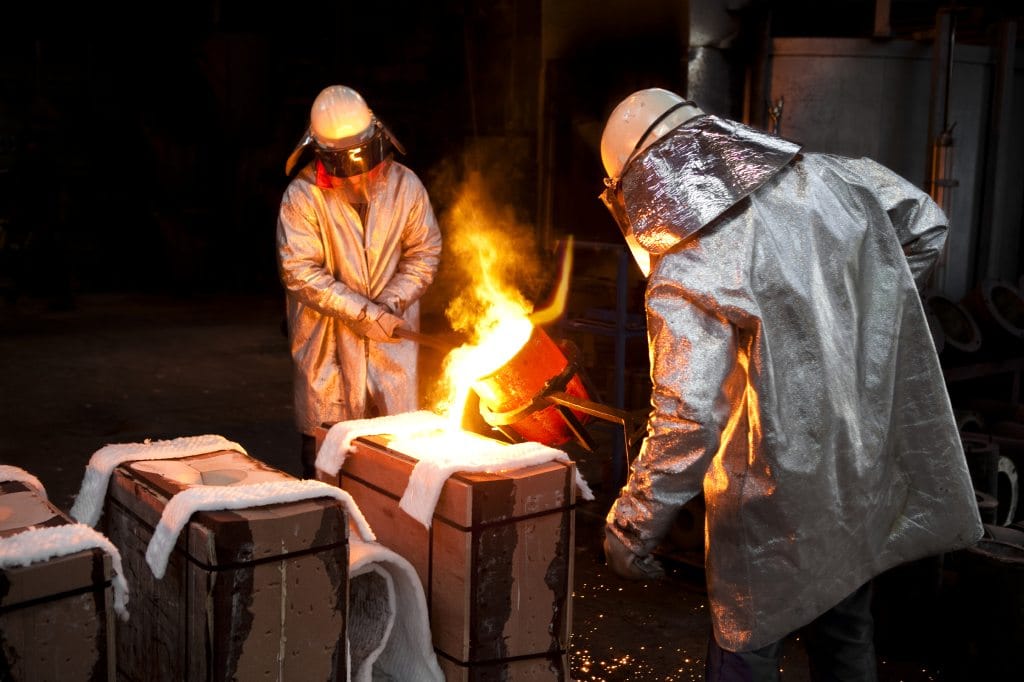

"Is this aluminized suit certified?"
It’s one of the most common—and critical—questions buyers ask.
In high-temperature industrial settings, compliance isn’t just paperwork—it’s protection.
Especially for aluminized PPE, where inadequate gear can lead to catastrophic burns, splash injuries, or regulatory fines.
Let’s break down the three key standards you need to know:
ASTM F955, NFPA 2112, and EN ISO 11612—and how to apply them to your sourcing decisions.
Why Standards Matter for Aluminized PPE
Every aluminized jacket or coverall claims to “reflect heat” or “protect from splash.”
But only the certified ones are actually tested to perform under real-world conditions.
Proper standards ensure the garment has:
- ✅ Passed independent lab testing
- ✅ Been labeled correctly for field use
- ✅ Met the minimum protection thresholds for heat, flame, and molten metal
⚠️ No certification = no entry on job sites, no passing audits, no worker safety.
ASTM F955: Molten Metal Splash Resistance
📍 Origin: USA (ASTM International)
🎯 Purpose: Test a garment’s resistance to molten metal splash
What it does:
- Simulates molten aluminum, iron, or copper being poured onto PPE
- Measures heat transfer, fabric integrity, and penetration
- Uses a calorimeter (skin simulant) to determine injury risk
Why it matters:
- Required in foundries, casting, and smelting
- Focuses on thermal exposure + splash pressure
✅ Look for garments labeled:
“Tested to ASTM F955 for molten aluminum at 1kg, 780°C”
NFPA 2112: Flash Fire Resistance
📍 Origin: USA (National Fire Protection Association)
🎯 Purpose: Protect workers from flash fire exposure (gas, vapor ignition)
What it does:
- Tests garments using a 3-second flash fire on a full mannequin
- Measures predicted body burn %
- Evaluates shrinkage, heat resistance, ignition time
Why it matters:
- Essential in oil & gas, refineries, and chemical plants
- Not all aluminized gear is NFPA 2112 compliant—must be tested specifically
✅ Valid garments will read:
“Certified to NFPA 2112 by [lab or manufacturer]”
EN ISO 11612: European Standard for Heat and Flame
📍 Origin: European Union (ISO + CEN)
🎯 Purpose: Provide performance levels for garments exposed to heat and/or flame
How it works:
This standard uses letter codes (A–F) with levels (1–3) to indicate protection.
| Code | Protection Type | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| A1/A2 | Flame spread resistance | Basic FR rating |
| B1–B3 | Convective heat | Furnace proximity |
| C1–C4 | Radiant heat | Glass or foundry work |
| D1–D3 | Molten aluminum splash | Aluminum smelting |
| E1–E3 | Molten iron splash | Steel casting |
| F1–F3 | Contact heat | Handling hot tools/surfaces |
Why it matters:
- Mandatory in Europe and many global projects
- Specifies exact performance by hazard type
- Higher number = higher protection
✅ Example label:
“EN ISO 11612: A1 B2 C3 D3 E2 F1”
Comparing the Three Standards
| Feature | ASTM F955 | NFPA 2112 | EN ISO 11612 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | USA | USA | Europe / Global |
| Hazard Focus | Molten splash | Flash fire | Heat, flame, molten splash |
| Test Type | Metal pour + heat | Full-body fire | Multiple lab tests |
| Radiant Heat | 🔸 Partial | 🔸 Indirect | ✅ Yes (C-rating) |
| Splash Protection | ✅ Primary | ❌ Not tested | ✅ (D/E rating) |
| Label Format | Descriptive | Certified logo | Lettered performance codes |
🧠 Bonus Tip: Some garments may carry multiple certifications for cross-market compatibility.
What to Ask Before You Buy
- Is the garment certified to ASTM, NFPA, or EN ISO standards?
- What metal type and weight was it tested with?
- Does it carry a valid test certificate? (request it!)
- Is it suitable for molten splash, radiant heat, and flame?
- Can it be worn with other PPE (e.g. helmet, gloves, respirator)?
- Is this label compliant with local law or site requirements?
At workwearsolutions, we ensure all aluminized gear can be matched to your regional compliance needs—with full documentation on hand.
Conclusion
If the label doesn’t say ASTM F955, NFPA 2112, or EN ISO 11612—it’s not real protection.
In high-heat work, standards are what separate true PPE from unsafe imitation.
As a buyer:
- Know what each standard tests and covers
- Match the certification to the hazard
- Ask for certificates—don’t rely on assumptions
- Choose suppliers who understand global PPE compliance
Need help sourcing aluminized PPE with verified compliance for your project or region? I’ll help you navigate the standards and select garments that keep your people—and your company—protected.
📩 Contact: [email protected]
🌐 Website: www.workwearsolutions.net
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
