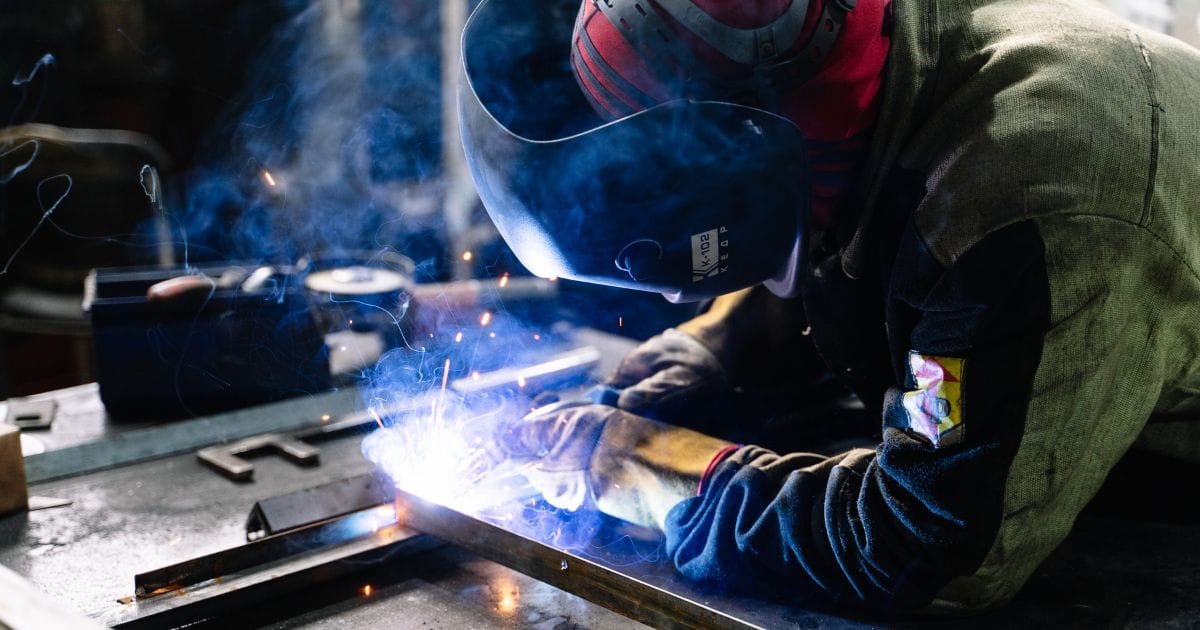

Not all welding processes are equal—and neither are their PPE requirements. Each welding method presents unique hazards such as spatter intensity, heat levels, and UV exposure. Choosing the wrong PPE can compromise safety, reduce productivity, and increase costs.
This guide breaks down PPE selection by welding process—so you can specify exactly what your team needs without overspending.
Why Process-Specific PPE Matters
- Stick Welding (SMAW): Produces heavy spatter and high heat.
- MIG Welding (GMAW): Moderate to heavy spatter, intense UV radiation.
- TIG Welding (GTAW): Minimal spatter but high radiant heat.
- Plasma Cutting: High temperature, sparks, and molten metal spray.
Using the same jacket or gloves across all processes might seem cost-effective, but it often leads to shortened garment life, discomfort, and non-compliance with safety standards.
Stick Welding (SMAW): Maximum Protection for Heavy Spatter
Hazards:
- Extremely hot sparks
- Heavy molten spatter
- Intense UV/IR radiation
Recommended PPE:
- Jacket: Full leather or leather-sleeved combo jackets
- Gloves: Thick leather, Kevlar® stitching, extended cuffs
- Apron: Optional for overhead welding
- Helmet: Auto-darkening with shade 10–14 lens
Pro Tip:
Consider Class 2 welding PPE under EN ISO 11611 for maximum protection in Stick welding environments.
Real-World Case:
A structural steel fabrication company reduced burn incidents by 80% after upgrading to leather jackets with reinforced seams for Stick welders.
MIG Welding (GMAW): Durable, Heat-Resistant PPE
Hazards:
- High spatter levels
- Strong arc radiation
- Medium to high heat load
Recommended PPE:
- Jacket: Leather or hybrid jackets (leather arms + FR cotton torso for mobility)
- Gloves: Heavy-duty MIG gloves with heat insulation
- Neck Protection: FR neck gaiter or bib
- Pants: FR-treated cotton with leather reinforcements
Buyer Tip:
Invest in ventilated jackets for MIG welders working long shifts—heat buildup is a major complaint.
TIG Welding (GTAW): Focus on Dexterity and Comfort
Hazards:
- Minimal spatter but high radiant heat
- Risk of burns from hot workpieces
- UV/IR exposure
Recommended PPE:
- Jacket: Lightweight FR cotton or aramid blend (breathable and flexible)
- Gloves: Thin TIG gloves for maximum finger control
- Eye Protection: Auto-darkening helmet with precise shade control (shade 8–12)
Pro Tip:
Avoid heavy leather for TIG—it restricts precision work and adds unnecessary heat stress.
Practical Scenario:
A precision welding shop switched from leather jackets to FR cotton jackets for TIG operations, improving worker dexterity and reducing fatigue complaints by 40%.
Plasma Cutting: Heat, Sparks, and High-Speed Particles
Hazards:
- Molten metal spray
- Extreme temperature cutting arc
- UV flash and glare
Recommended PPE:
- Jacket: Leather or leather-hybrid for heavy-duty cutting
- Gloves: Heat-resistant, full-coverage gloves
- Face Shield: In addition to welding helmet for flying debris
- Leg Protection: Leather spats or FR leggings
Buyer Tip:
Consider garments with double-layer knee protection for plasma cutting work done in kneeling positions.
Quick PPE Selection Matrix by Process
| Process | Jacket Material | Gloves Type | Additional PPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stick Welding | Full Leather | Heavy-duty leather | Apron, FR leggings |
| MIG Welding | Leather/Hybrid | MIG gloves | Neck gaiter, reinforced pants |
| TIG Welding | FR Cotton/Aramid | TIG gloves | Lightweight helmet accessories |
| Plasma Cutting | Leather/Leather Blend | Heat-resistant gloves | Face shield, knee pads |
Compliance and Standards
- ANSI Z49.1: U.S. welding safety guidelines
- EN ISO 11611: Specifies Class 1 (light welding) and Class 2 (heavy welding) garments
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.252: Requires PPE for welding and cutting operations
Always verify class and certification based on the welding process before purchasing.
Buyer FAQs
Q: Can we standardize PPE for all welding tasks to save money?
A: No. Over-specifying for light processes (e.g., TIG) causes discomfort; under-specifying for heavy processes (Stick, Plasma) compromises safety.Q: How do I know if garments meet EN ISO 11611 Class 2?
A: Look for the Class 2 mark on labels and request compliance certificates from your supplier.Q: Can TIG gloves be used for MIG welding?
A: No. TIG gloves prioritize dexterity over heat protection, making them unsafe for MIG or Stick welding.
Conclusion
PPE selection should match the welding process to ensure optimal safety, compliance, and comfort. Stick welding needs maximum protection, TIG prioritizes dexterity, MIG demands heat resistance, and plasma cutting requires robust shielding against sparks and particles.
Need expert advice or a full PPE kit recommendation for your welding team?
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.workwearsolutions.net
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
