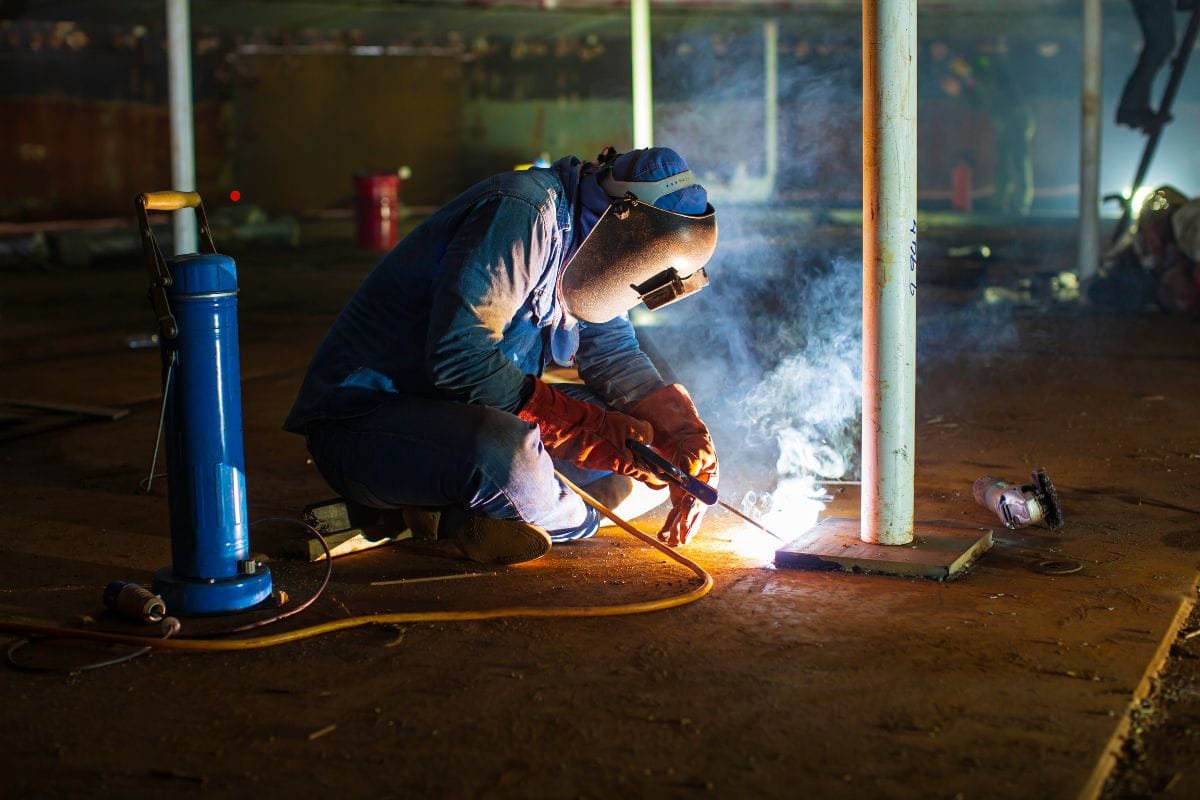

When it comes to welding protective clothing, the fabric you choose matters as much as the design. Using the wrong material can lead to catastrophic consequences: ignition, melting, or rapid fabric breakdown under high heat. On the other hand, the right choice guarantees protection, comfort, and compliance, reducing workplace injuries and saving costs in the long run.
This guide takes a deep dive into the most widely used welding PPE fabrics—leather, FR cotton, aramids, and blends—with practical examples, cost considerations, and performance comparisons.
Why Fabric Selection Matters
Welding exposes workers to multiple hazards, and the fabric on their back is the first shield:
- Sparks and Spatter: Tiny molten metal droplets (often over 1,500°C) that can ignite unprotected fabrics.
- Infrared & UV Radiation: Breaks down fabrics, weakens fibers, and causes severe skin burns if PPE fails.
- Mechanical Wear: Abrasive metal edges and tools shorten garment life if fabric isn’t durable.
- Chemical Contaminants: Oil or solvents on untreated fabrics can lead to flash ignition.
Real Incident:
In 2022, a welder suffered second-degree burns when synthetic polyester underlayers melted into his skin during overhead Stick welding. The outer jacket was not FR-rated and failed instantly upon spatter contact.
Lesson: Never allow synthetics near welding operations unless they are inherently flame-resistant.
Regulatory Reminder:
Standards like EN ISO 11611 and ANSI Z49.1 require flame-resistant, non-melting fabrics for welding PPE.
1. Leather: The Gold Standard for Heavy-Duty Welding
Why Leather?
Leather has been the industry benchmark for decades due to its natural flame and heat resistance, thickness, and toughness.
Advantages:
- Exceptional thermal protection for Stick and MIG welding
- Long-lasting durability under heavy mechanical stress
- Excellent for high-spatter applications
Drawbacks:
- Heavy, less breathable—can lead to heat stress in hot climates
- Requires maintenance (oil treatments to prevent drying and cracking)
- Higher cost compared to FR cotton
Real-World Example:
Shipbuilding yards and structural steel fabrication shops almost exclusively use full-leather jackets and aprons for Stick welding because spatter frequency and temperature can easily compromise lighter fabrics.
Best For:
- Stick welding (SMAW)
- MIG welding
- Oxy-fuel cutting and gouging
2. FR Cotton: Lightweight Comfort for Light-Duty Tasks
Why FR Cotton?
FR-treated cotton garments offer a lightweight, breathable solution for less intense welding operations. They self-extinguish when exposed to sparks and flames—making them a safe and economical choice.
Advantages:
- Affordable and widely available
- Comfortable for long shifts in moderate heat
- Easy to wash and maintain
Limitations:
- FR treatment can diminish after 50–100 washes
- Not suitable for high-spatter welding like Stick or heavy MIG
- Requires strict laundering with FR-safe detergents
Use Case:
An automotive component plant adopted FR cotton jackets for TIG welding operations in confined spaces. Workers reported 30% higher comfort and reduced fatigue compared to heavy leather jackets, which were previously over-specified for the task.
Best For:
- TIG welding
- Grinding or light fabrication
- Welding inside climate-controlled facilities
3. Aramid Fabrics (Kevlar®, Nomex®): High-Tech Protection
Why Aramids?
Aramid fibers like Kevlar® and Nomex® deliver inherent flame resistance, superior strength-to-weight ratio, and remarkable durability under high heat.
Advantages:
- FR properties do not wash out
- Excellent cut, puncture, and abrasion resistance
- Lightweight compared to leather, yet highly protective
Limitations:
- Expensive upfront investment
- Susceptible to UV degradation if stored improperly
- Requires specialized washing
Practical Application:
Offshore oil rigs and energy companies often choose aramid-blend garments because they provide dual compliance: FR for fire hazards and cut resistance for rope and steel cable handling.
Best For:
- Environments demanding multi-hazard protection (heat + mechanical + FR)
- Premium gloves and welding sleeves for high-risk jobs
4. Blended Fabrics and Modern Innovations
Many manufacturers now offer hybrid solutions, combining the best properties of different materials:
- FR Cotton + Nylon Blends: Improved durability without sacrificing comfort
- Leather-Reinforced Jackets: Leather sleeves paired with FR cotton bodies for mobility and thermal protection
- Carbon or Para-Aramid Inserts: Added heat protection in high-impact zones
Trend Alert:
Some high-performance garments now integrate moisture-wicking layers under FR fabrics to combat heat stress—a major advantage for welders working long shifts in warm environments.
Fabric Performance Comparison Table
| Fabric Type | Heat Resistance | Comfort | Durability | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leather | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | $$$ |
| FR Cotton | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | $ |
| Aramid (Kevlar®) | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | $$$$ |
| FR Blends | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | $$-$$$ |
Key Factors Before Purchasing
- Process Type: Stick/MIG = Leather or leather-hybrid; TIG = FR cotton or blends
- Work Environment: Outdoor vs. indoor, humidity, ambient temperature
- Safety Compliance: Check EN ISO 11611 Class 1/2 or ANSI Z49.1 certification
- Budget Consideration: Calculate total cost of ownership vs. upfront cost
Buyer FAQs (Expanded)
Q: Can polyester FR fabrics replace leather for heavy welding?
A: No. Even FR polyester can degrade at high spatter temperatures. Leather or leather-blend is still required for heavy-duty welding.Q: Does FR cotton lose its flame resistance after repeated washing?
A: Yes, after 50–100 cycles depending on treatment. Always replace garments that fail FR testing.Q: Why invest in expensive aramid fabrics?
A: For environments where durability, heat protection, and mechanical strength are critical, the higher cost offsets reduced replacement frequency.
Conclusion
Fabric choice defines the safety, comfort, and cost-effectiveness of welding PPE. Leather dominates heavy-duty jobs, FR cotton fits light-duty roles, and aramids provide cutting-edge protection for multi-hazard environments. Blended solutions offer a balance for dynamic workflows.
Need expert advice on selecting the right welding PPE fabric for your operations?
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.workwearsolutions.net
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
