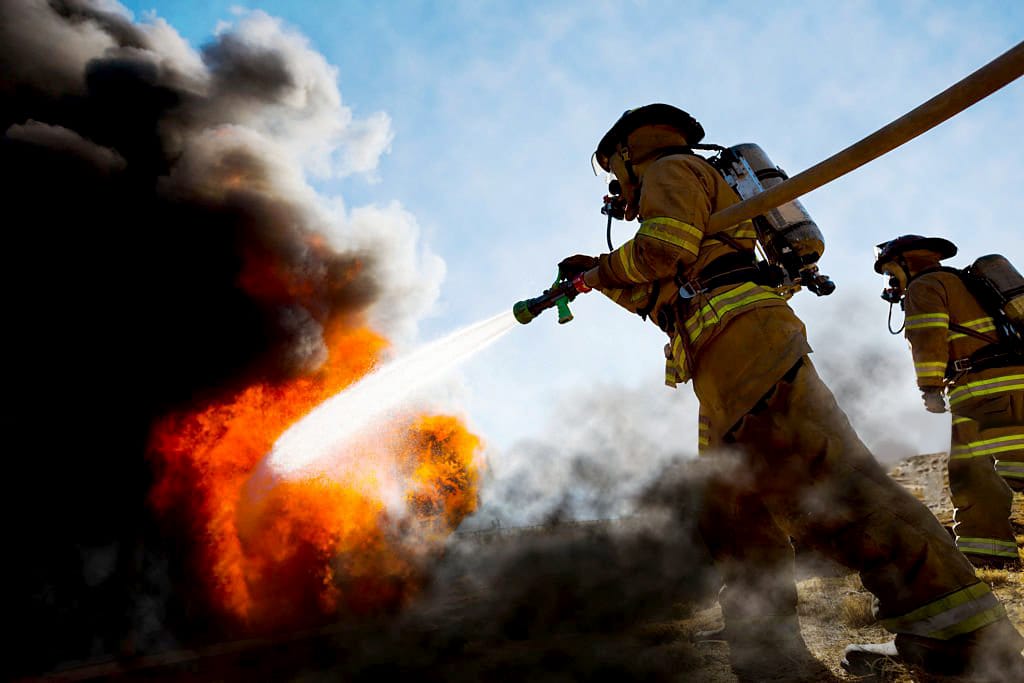

Flame-resistant (FR) clothing is specifically designed to protect workers from burns and injuries in environments where they might be exposed to flames, sparks, or intense heat. Unlike regular fabrics, flame-resistant materials are either inherently resistant to burning or treated with chemicals to self-extinguish when exposed to fire. This makes FR clothing critical for worker safety in industries with high fire risk, such as oil and gas, electrical work, and welding.
Flame-resistant clothing provides a protective barrier that reduces burn injuries by minimizing the spread of flames and limiting direct exposure to extreme heat.
What is Considered Flame-Resistant Clothing?
Flame-resistant clothing refers to garments that are constructed from materials designed to withstand ignition and self-extinguish when exposed to flames.
FR clothing includes items like coveralls, jackets, pants, and shirts made from fire-resistant fabrics like Nomex, Kevlar, or flame-retardant-treated cotton.
| Type of FR Clothing | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| FR Coveralls | Full-body suits providing maximum coverage | Oil & gas, chemical handling |
| FR Jackets | Flame-resistant outerwear for upper body | Welding, electrical work |
| FR Pants | Lower-body protection against sparks/heat | Manufacturing, construction |
| FR Shirts | Everyday work shirts with fire resistance | Electrical, utility work |
Common Features of FR Clothing:
- Self-Extinguishing Properties: The material stops burning once the ignition source is removed, reducing injury risk.
- Heat Resistance: Protects the skin from direct heat exposure.
- Durability: Maintains integrity after repeated exposure to flames or high temperatures.
Why is Fire-Resistant Clothing So Important?
Fire-resistant clothing is essential because it provides a vital layer of protection that can mean the difference between life and death in hazardous work environments.
FR clothing is important as it reduces the risk of severe burns, prevents clothing from melting to the skin, and allows workers extra time to escape fire hazards.
Key Benefits of FR Clothing:
- Burn Prevention: By reducing the risk of severe burns, FR clothing minimizes recovery time and potential scarring.
- Temperature Protection: Protects against extreme heat and prevents injuries from direct flame exposure.
- Compliance: Meets industry-specific safety standards, which is often a legal requirement in high-risk industries.
In environments with exposure to flames or high temperatures, FR clothing helps protect workers from the immediate effects of fire, reducing the severity of injuries.
How Does Flame-Resistant Clothing Work?
Flame-resistant clothing works by either using fabrics that are inherently resistant to flames or materials treated with flame-retardant chemicals.
When exposed to fire, FR clothing resists ignition and self-extinguishes once the flame source is removed.
Mechanism of Flame Resistance:
- Inherent Flame Resistance: Some materials, like Nomex and Kevlar, are naturally resistant to burning due to their chemical structure.
- Chemical Treatment: Cotton or other fabrics may be treated with flame-retardant chemicals that prevent the material from igniting.
- Thermal Insulation: FR materials act as a barrier, keeping intense heat away from the skin.
This design helps FR clothing prevent secondary burns by not melting or dripping when exposed to fire, unlike synthetic fibers.
Who Needs to Wear FR Clothing?
FR clothing is mandatory for workers in high-risk industries where exposure to flames, heat, or electrical hazards is common.
Industries that require FR clothing include oil and gas, welding, electrical utilities, manufacturing, and emergency response.
| Industry | Common FR Clothing Needed | Hazard Types |
|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | FR coveralls, jackets | Fire, flash fires, explosions |
| Welding | FR jackets, aprons, gloves | Sparks, open flames |
| Electrical Utilities | FR shirts, pants, coveralls | Arc flashes, electrical burns |
| Manufacturing | FR shirts, pants | Chemical splashes, industrial fires |
| Emergency Response | FR jackets, gloves | Fire, intense heat |
Workers Who Require FR Clothing:
- Electricians: Exposure to arc flashes requires clothing that can withstand electrical bursts.
- Welders: FR aprons and jackets protect against sparks and molten metal.
- First Responders: Firefighters and rescue workers rely on FR clothing to protect against flames in emergency situations.
Workers in these roles face potential exposure to fire or extreme heat regularly, making FR clothing a key part of their PPE.
What Fabric is Most Flame Resistant?
Some fabrics are inherently more flame-resistant, while others achieve fire resistance through treatments.
Nomex, Kevlar, and other aramid fibers are the most flame-resistant materials, while treated cotton offers a more affordable option for moderate-risk environments.
| Fabric Type | Flame Resistance Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nomex | Inherent flame resistance | Oil and gas, military, firefighting |
| Kevlar | High heat resistance, durability | Electrical, welding, industrial work |
| Modacrylic | Self-extinguishing, comfortable | Electrical, chemical processing |
| Treated Cotton | Flame-retardant-treated, affordable | General manufacturing, utility work |
Comparison of Common FR Fabrics:
- Nomex and Kevlar: Aramid fibers are strong, lightweight, and inherently flame-resistant, making them ideal for high-risk environments.
- Modacrylic: Blended with other materials, it offers good fire resistance with added comfort.
- Treated Cotton: Cost-effective and flame-retardant treated, making it suitable for workers with lower exposure risks.
While inherently flame-resistant fabrics are more durable, treated cotton is often preferred for cost-efficiency in industries with moderate fire hazards.
Why is Flame-Resistant Clothing So Expensive?
FR clothing can be costly due to the specialized materials, manufacturing processes, and stringent testing required to ensure quality and safety.
Flame-resistant clothing is expensive because it uses high-performance fabrics and undergoes rigorous testing to meet industry standards for protection.
Factors Contributing to FR Clothing Cost:
- Specialized Materials: Inherently flame-resistant fibers like Nomex and Kevlar are more costly to produce.
- Chemical Treatments: Treated cotton involves additional manufacturing steps to add flame-retardant chemicals.
- Durability Standards: FR clothing is made to withstand extreme conditions, which requires advanced technology and testing.
- Certification Requirements: Testing and certification to meet standards like NFPA 2112 or ASTM F1506 add to production costs.
Why the Cost is Worth It:
Investing in quality FR clothing reduces the likelihood of severe burns, costly medical bills, and downtime due to injuries. This makes it a necessary expense in high-risk industries where fire hazards are part of daily operations.
Conclusion
Flame-resistant clothing is an essential protective measure for workers in high-risk environments where exposure to fire, intense heat, and electrical arcs is common. With materials like Nomex, Kevlar, and treated cotton, FR clothing offers a barrier that self-extinguishes to minimize burns and injuries. It is especially important for workers in industries such as oil and gas, electrical utilities, and emergency response. Although more expensive than standard workwear, the protection provided by flame-resistant clothing justifies the cost by reducing injury risks and providing peace of mind for workers and employers alike.
By understanding the specific needs for FR clothing in different roles and selecting the right fabrics, companies can enhance workplace safety, protect their workforce, and ensure compliance with industry safety standards.
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
