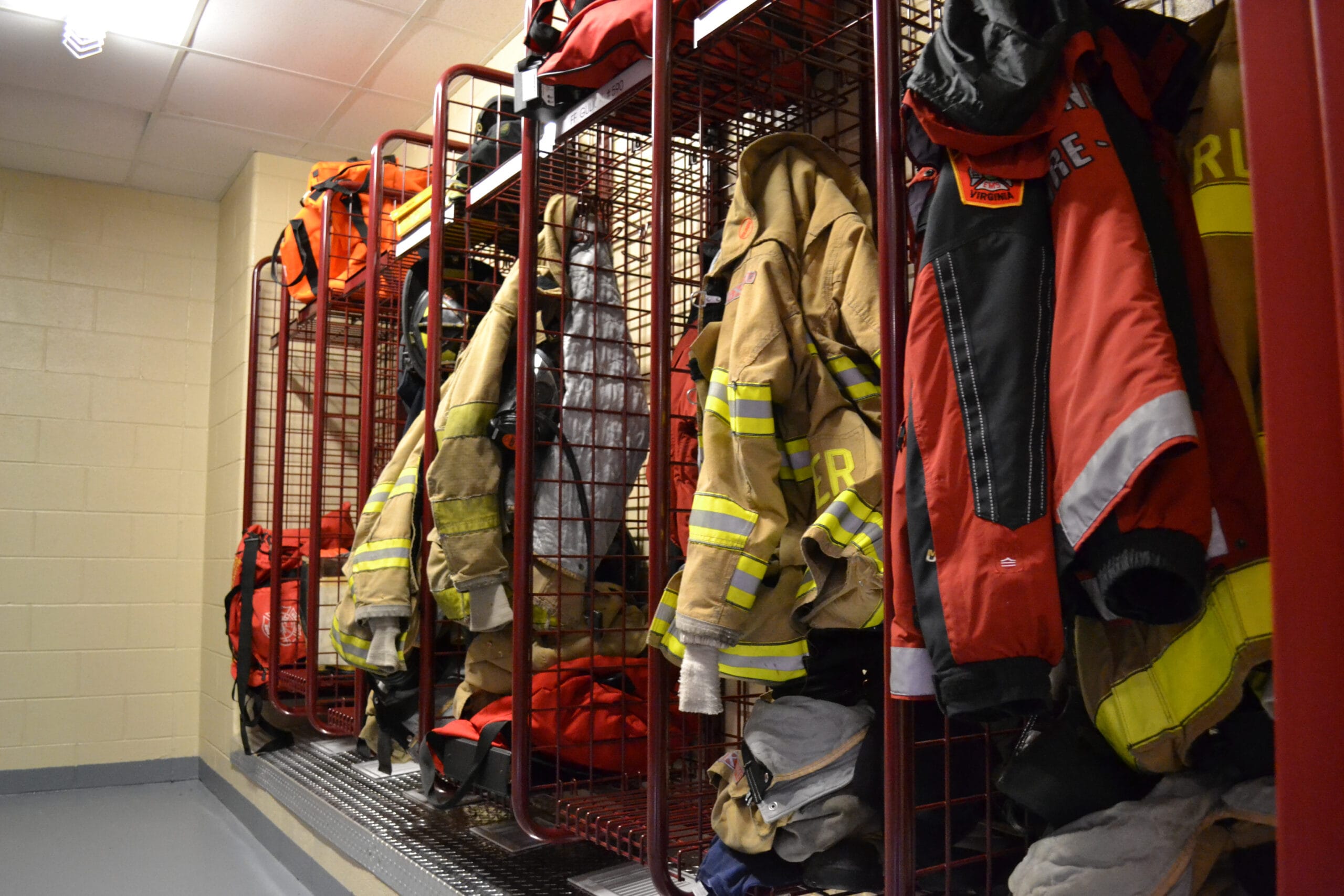

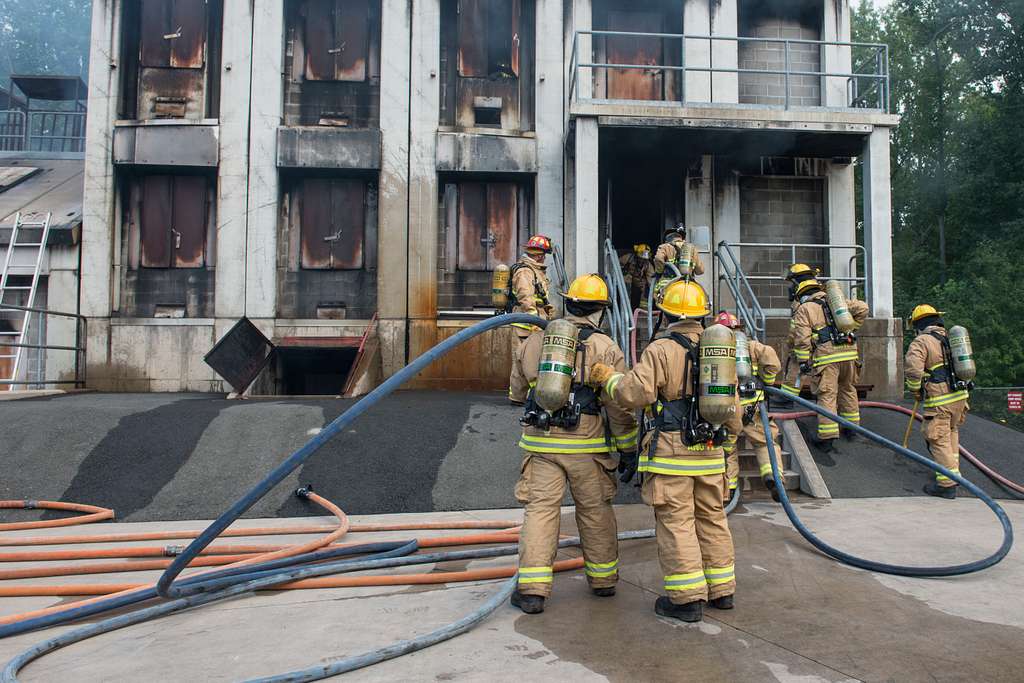
Firefighting is one of the most hazardous professions, exposing individuals to extreme heat, toxic gases, and dangerous environments. Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)1 is vital to ensure the safety and effectiveness of firefighters during operations. From head-to-toe protection2 to innovative advancements, firefighting PPE is designed to withstand intense conditions and save lives.
Firefighting PPE includes turnout gear, helmets, gloves, boots, and respiratory equipment, each tailored to protect against extreme heat, toxic gases, and physical hazards. Advanced materials like Nomex and Kevlar enhance heat resistance and durability, while innovations like integrated cooling systems improve mobility and comfort.
What are the essential components of a firefighter’s PPE ensemble?
Firefighters rely on a full set of specialized PPE to protect them from heat, debris, and hazardous substances during operations.
A firefighter’s PPE ensemble includes turnout gear, helmets, gloves, boots, and respiratory equipment, each designed to shield against specific hazards.
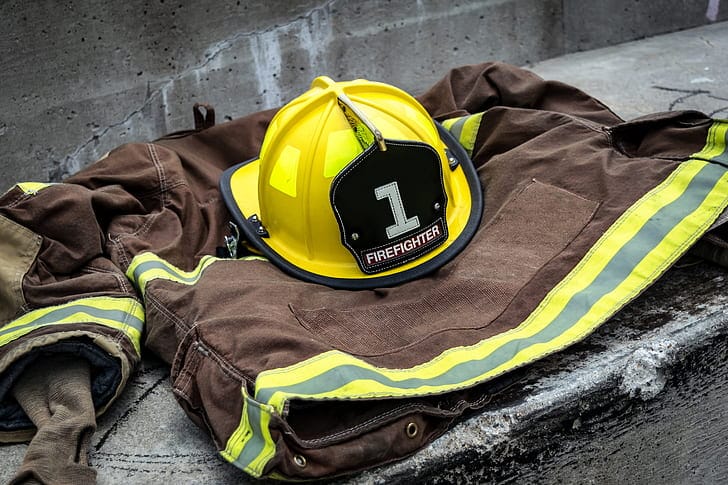

The key components of firefighting PPE are:
-
- Includes a flame-resistant coat and pants made from materials like Nomex or Kevlar.
- Provides thermal protection and shields against debris.
-
Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA)4:
- Supplies breathable air in smoke-filled or toxic environments, allowing firefighters to operate safely.
-
Helmet:
- Made from heat-resistant materials to protect the head from falling objects and extreme heat.
- Often includes visors or goggles for eye protection.
-
Gloves:
- Designed to resist high temperatures while maintaining dexterity for handling tools and hoses.
-
Boots:
- Made with steel toes and slip-resistant soles to protect against sharp objects and uneven terrain.
Each piece is critical in creating a protective barrier against the multiple risks firefighters face.
What role do flame-resistant fabrics play in firefighting PPE?
Flame-resistant fabrics are the cornerstone of firefighting PPE, providing essential protection against intense heat and flames.
Materials like Nomex and Kevlar are integral to firefighting PPE, offering durability, thermal resistance, and the ability to withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
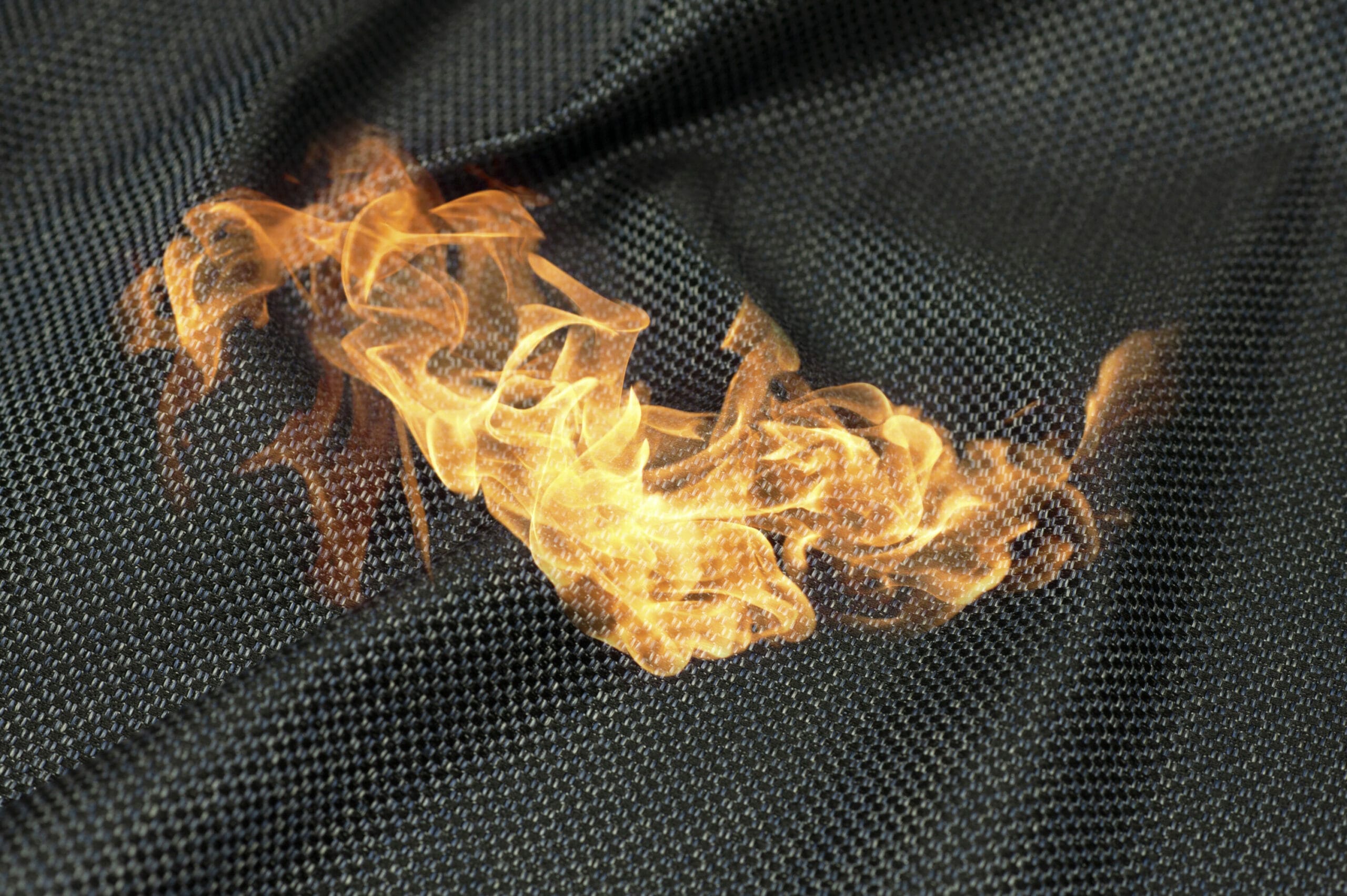

Key flame-resistant materials include:
| Material | Features | Usage in PPE |
|---|---|---|
| Nomex5 | Lightweight, durable, and heat-resistant | Turnout gear, gloves |
| PBI6 | Exceptional thermal and chemical resistance | Outer layers of turnout gear |
- Heat Protection: Shields against temperatures over 500°F.
- Durability: Maintains integrity after repeated exposure to heat and flames.
- Lightweight: Enhances mobility and reduces fatigue during operations.
These fabrics are essential in ensuring that firefighting PPE remains effective under extreme conditions.
How does PPE for structural firefighting differ from wildland firefighting?
The nature of structural and wildland firefighting requires different PPE tailored to the unique hazards of each environment.
Structural firefighting PPE is heavier and more heat-resistant, while wildland firefighting gear prioritizes mobility and breathability for outdoor operations.
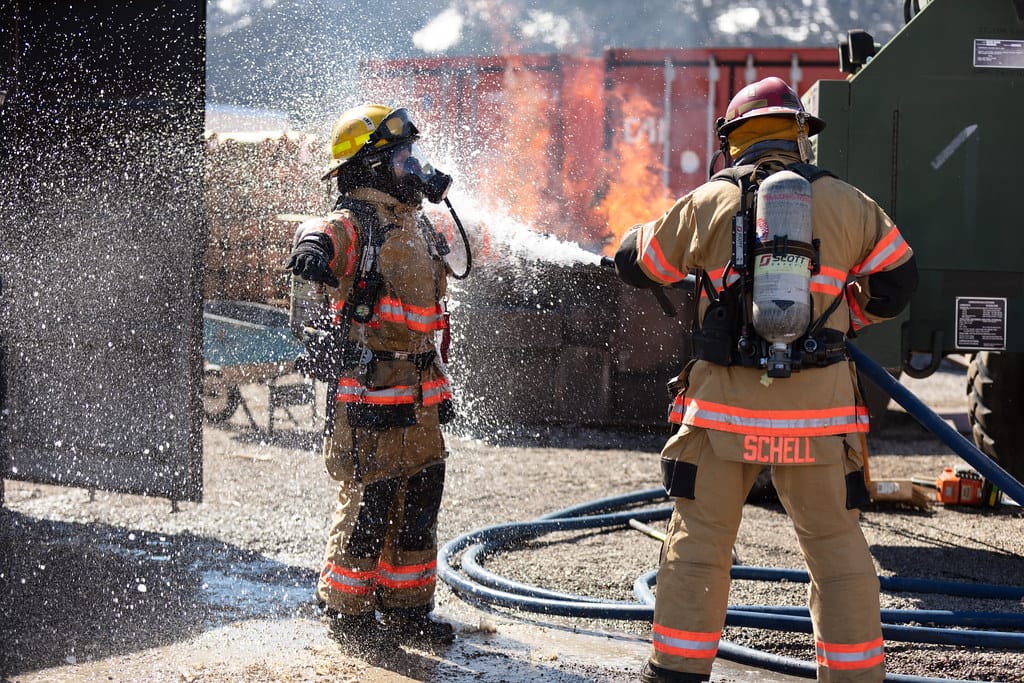

Structural Firefighting PPE:
- Focuses on protection against high temperatures, falling debris, and confined spaces.
- Includes:
- Thick turnout gear7 for thermal insulation.
- Heavy-duty helmets with visors.
- SCBA systems8 for respiratory protection in smoke-filled environments.
Wildland Firefighting PPE:
- Prioritizes lighter materials for extended wear in outdoor, high-mobility scenarios.
- Includes:
- Fire-resistant shirts and pants made from Nomex.
- Protective goggles to shield against ash and debris.
- Lightweight helmets9 designed for comfort in long shifts.
Understanding these differences ensures that firefighters are equipped appropriately for their specific mission.
What are the international standards for firefighting PPE, and how do they ensure safety?
Global standards set strict guidelines to ensure firefighting PPE meets safety and performance requirements.
Standards like NFPA 1971 and ISO 11999 ensure that firefighting PPE is tested for heat resistance, durability, and overall effectiveness.

Key Standards:
-
NFPA 1971 (U.S.):
- Covers the minimum requirements for structural and proximity firefighting gear.
- Includes testing for heat resistance, thermal insulation, and tear strength.
-
ISO 11999 (International):
- Provides global guidelines for firefighting PPE design and performance.
- Focuses on ergonomics, durability, and protection levels.
-
EN 469 (Europe):
- Defines requirements for protective clothing used in firefighting.
- Emphasizes thermal protection and liquid resistance.
These standards ensure that PPE meets the necessary benchmarks for safety, offering confidence to firefighters and their organizations.
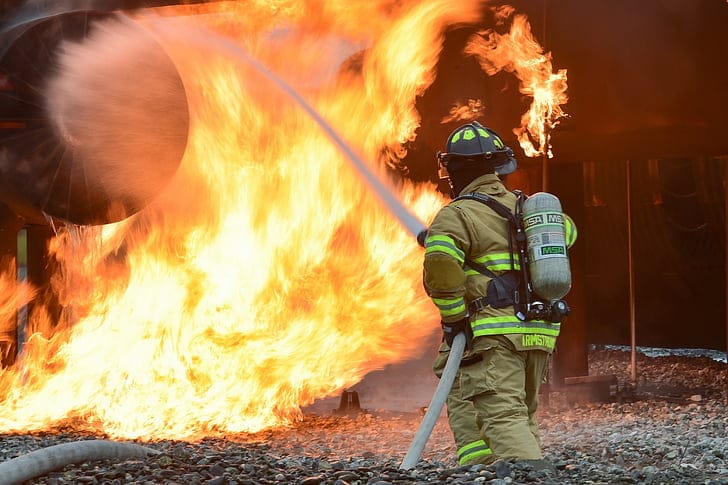
What advancements in firefighting PPE are enhancing safety and mobility?
Innovations in firefighting PPE are improving safety, comfort, and operational efficiency through the integration of advanced materials and technology.
Advancements like smart helmets, lightweight materials, and integrated cooling systems are revolutionizing firefighting PPE, offering better protection and mobility.

Notable Innovations:
-
- Equipped with communication systems and thermal imaging for enhanced situational awareness.
-
Advanced Fabrics:
- Lightweight, flexible materials that maintain high thermal protection.
- Enhanced breathability reduces heat stress during extended operations.
-
Cooling Systems:
- Integrated cooling vests that regulate body temperature in high-heat conditions.
-
- Monitor vital signs such as heart rate and body temperature.
- Provide real-time alerts to prevent overexertion or heat exhaustion.
-
Ergonomic Designs:
- Improved fit and reduced weight to enhance mobility and reduce fatigue.
These advancements are critical in addressing the evolving challenges faced by modern firefighters.
Conclusion
Firefighting PPE is a crucial line of defense against the extreme hazards faced by firefighters. From essential components like turnout gear and helmets to innovative advancements such as smart technology and cooling systems, PPE ensures that firefighters can perform their duties safely and effectively. Adhering to international standards and leveraging modern designs, firefighting PPE continues to evolve, offering greater protection and comfort in the line of duty.
-
Linking this keyword provides an overview of the critical gear firefighters use to protect themselves from heat, toxic gases, and structural hazards during operations. ↩
-
This keyword emphasizes the full range of protective gear, ensuring readers understand the comprehensive measures needed for firefighter safety in high-risk environments. ↩
-
Linking this keyword to provide detailed insights into the advanced fabrics like Nomex and Kevlar, explaining their effectiveness in extreme conditions. ↩
-
Linking this keyword helps explain the importance of SCBA in providing breathable air, which is essential for survival and effectiveness during firefighting operations. ↩
-
Linking this keyword to explain how Nomex’s lightweight and heat-resistant properties contribute to its effectiveness in firefighting gear, such as turnout coats and gloves. ↩
-
Linking this keyword provides insights into the advanced capabilities of PBI, particularly its role in protecting firefighters from both extreme heat and hazardous chemicals. ↩
-
Linking this keyword to explain how thick turnout gear provides insulation and shields firefighters from extreme heat and debris in confined and hazardous environments. ↩
-
Linking this keyword highlights how lightweight helmets are designed for comfort, mobility, and extended wear in outdoor scenarios, which are critical for wildland firefighters. ↩
-
This keyword is essential for understanding how respiratory systems enable firefighters to breathe safely in toxic and low-oxygen conditions during structural firefighting missions. ↩
-
Linking this keyword to highlight how technology, such as built-in communication systems and thermal imaging, improves efficiency and safety during firefighting operations. ↩
-
Linking this keyword provides insights into how wearable technology can track vital signs and issue alerts, enabling proactive measures to ensure firefighter well-being in high-stress environments. ↩
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
