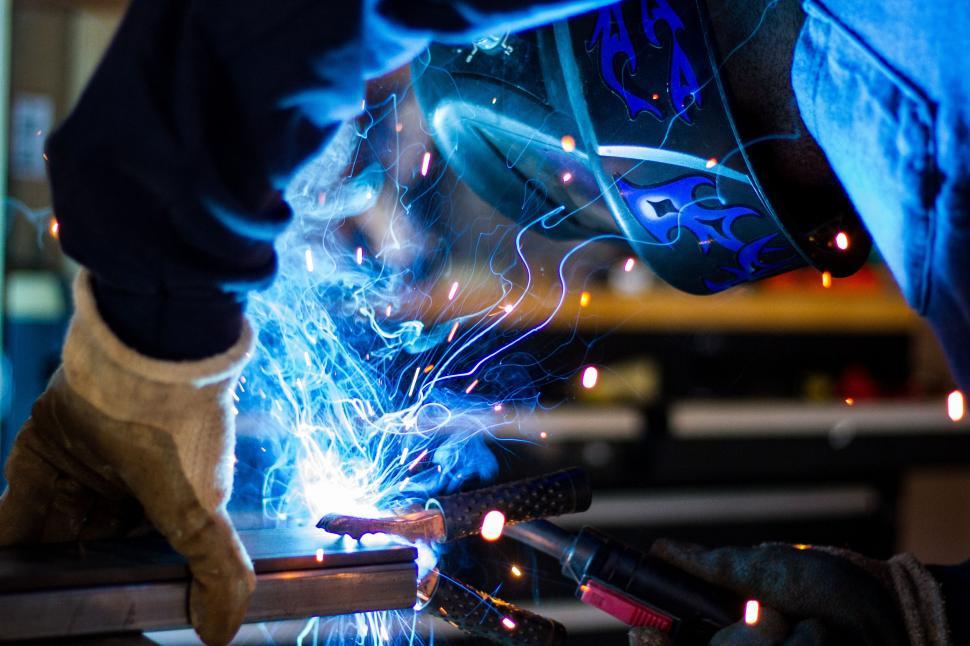

Selecting the right welding gloves is a critical decision that directly impacts both safety and performance. Welding projects are inherently hazardous, involving high temperatures, flying sparks, sharp edges, and the constant risk of burns or abrasions. Gloves act as the first line of defense, shielding hands from these dangers while allowing the welder to maintain control over their tools and materials. However, not all welding gloves are created equal.
The perfect welding gloves depend on several factors, including the type of welding being performed, the specific demands of the project, and the welder’s personal comfort needs. For example, some welding tasks may prioritize high heat resistance, while others require enhanced dexterity for precision work. Balancing protection with functionality is key; gloves that are too bulky may hinder movement, while overly thin gloves may fail to provide adequate protection.
In addition to these practical considerations, the material, fit, and durability of welding gloves play a crucial role in ensuring long-lasting performance. Whether you’re working on heavy-duty structural welding or intricate artistic projects, choosing the right gloves can enhance productivity, reduce fatigue, and most importantly, protect against potential injuries.
When selecting welding gloves, it’s not just about picking a pair that looks durable—it’s about finding the right combination of safety, comfort, and efficiency tailored to the demands of your specific welding environment.

What are the key materials used in welding gloves, and how do they impact performance?
Welding gloves are crafted from a variety of durable and heat-resistant materials, each chosen to provide protection against the intense conditions of welding environments. These materials are designed not only to shield hands from high temperatures, sparks, and abrasions but also to ensure that welders can maintain the necessary dexterity and grip for their tasks.
The most common materials used in welding gloves include cowhide, deerskin, goatskin, and pigskin, each offering unique features that cater to different welding techniques and work environments. Understanding the properties of these materials is essential for selecting gloves that strike the right balance between safety, comfort, and functionality.
Material Properties and Their Impact on Performance
| Material | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Cowhide | Heat-resistant, durable, flexible | General welding, including MIG and stick |
| Deerskin | High dexterity, comfortable, resistant to punctures | TIG welding requiring precision |
| Goatskin | Lightweight, abrasion-resistant, excellent grip | TIG welding1 and detailed tasks |
| Pigskin | Breathable, oil-resistant, durable in wet conditions | Outdoor and heavy-duty welding tasks2 |
In-Depth Material Analysis
-
Cowhide3:
Cowhide is one of the most popular materials for welding gloves due to its exceptional durability and heat resistance. It is thick enough to provide protection from sparks and heat while remaining flexible for easy hand movement.- Advantages: Excellent for heavy-duty welding, provides long-lasting durability.
- Ideal Uses: Commonly used in MIG and stick welding, where exposure to high temperatures and flying sparks is frequent.
-
Deerskin:
Deerskin offers superior dexterity and comfort, making it a favorite for tasks requiring precision. Its natural flexibility allows welders to maintain fine motor control without sacrificing protection.- Advantages: Soft, lightweight, and puncture-resistant.
- Ideal Uses: Perfect for TIG welding and intricate jobs where precise hand movements are critical.
-
Goatskin4:
Goatskin is valued for its lightweight nature and excellent abrasion resistance. Its natural lanolin content gives it a softer texture while maintaining strength and durability.- Advantages: Provides a firm grip and reduces hand fatigue during extended use.
- Ideal Uses: Commonly used in TIG welding and tasks requiring delicate handling.
-
Pigskin:
Pigskin is known for its breathability and resistance to oil and moisture, making it an excellent choice for outdoor or damp conditions. Its natural texture provides a good grip, even in challenging environments.- Advantages: Durable in wet or greasy settings, resists cracking and hardening.
- Ideal Uses: Suitable for heavy-duty welding, maintenance work, and outdoor welding projects.
Matching Materials to Your Welding Needs
Choosing the right material depends on the type of welding and the specific challenges of your work environment. For high-heat welding like stick or MIG, cowhide offers unmatched protection. In contrast, TIG welders benefit from the flexibility and precision provided by deerskin or goatskin. If you’re working in outdoor or wet conditions, pigskin gloves are the ideal solution.
Tip: When selecting welding gloves, always consider the balance between protection and dexterity. A glove that fits the demands of your task will not only enhance safety but also improve your overall efficiency and comfort.
By understanding the properties of different materials, you can ensure that your welding gloves provide the right level of performance for your specific projects.

What are the differences between MIG, TIG, and stick welding gloves?
Welding gloves are not one-size-fits-all. Each welding technique—MIG, TIG, and stick welding—presents unique challenges and hazards that require specific types of gloves. Understanding these differences helps ensure both safety and performance during welding projects. Below, we dive into the distinct characteristics and purposes of gloves designed for each method.
MIG Welding Gloves
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding involves high heat levels, sparks, and spatter, making robust protection a priority. Gloves for MIG welding are designed with durability and safety in mind:
- Features: MIG gloves are thick, offering excellent protection against intense heat, molten metal spatter, and abrasion. Their robust construction minimizes the risk of burns or cuts.
- Design: These gloves are typically loose-fitting to provide a buffer against heat and spatter. The looser fit also enhances comfort during prolonged sessions.
- Materials5: MIG gloves are often made from durable materials like cowhide or pigskin, chosen for their heat resistance and long lifespan.
Example Use Case: A welder working on heavy steel fabrication requires gloves that can endure continuous high heat while providing ample protection against sparks.
TIG Welding Gloves
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is all about precision and control. This technique generates less spatter than MIG but demands greater dexterity for handling the torch and filler rods.
- Features: TIG gloves are lightweight and prioritize flexibility over heavy-duty protection. They allow for precise movements, making them ideal for intricate welding tasks.
- Design: These gloves have a snug fit to enhance finger mobility and tactile feedback, critical for maintaining control during fine work.
- Materials: Typically crafted from soft and pliable materials like goatskin or deerskin6, TIG gloves strike a balance between comfort and functionality.
Example Use Case: An artist welding intricate metal sculptures would benefit from TIG gloves, as they enable delicate hand movements without compromising protection.
Stick Welding Gloves
Stick welding, also known as SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding), is the most rugged of the three methods, producing extremely high temperatures, heavy spatter, and molten metal. Gloves for stick welding must offer the highest level of protection.
- Features: These gloves are heavy-duty and designed to withstand extreme heat and abrasion. They include thick padding for enhanced safety.
- Design: Stick welding gloves are generally bulkier, with reinforced areas to protect against molten metal and prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
- Materials: Cowhide is the most common material, valued for its superior durability and heat resistance. Some gloves may also feature insulated linings for added protection.
Example Use Case: A construction welder repairing industrial equipment in harsh outdoor conditions would require stick welding gloves to endure heavy spatter and intense heat.
Why Choosing the Right Glove Matters
The right gloves ensure not only safety but also efficiency. A mismatch between gloves and the welding technique can lead to discomfort, reduced precision, or even accidents.
| Welding Method | Key Hazards | Ideal Glove Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | High heat, sparks, spatter | Thick, durable, loose-fitting gloves made of cowhide or pigskin |
| TIG Welding | Precision work, lower heat | Lightweight, snug-fitting gloves made of goatskin or deerskin |
| Stick Welding | Extreme heat, heavy spatter | Heavy-duty, highly heat-resistant gloves made of cowhide |
By understanding the unique requirements of each welding method, welders can select gloves that enhance safety and performance, tailored to their specific needs.

What safety standards should welding gloves meet to ensure protection?
Welding gloves play a critical role in safeguarding welders from a range of hazards, including extreme heat, electrical shocks, and mechanical injuries such as cuts and punctures. To ensure these gloves provide the necessary level of protection, they must meet stringent safety standards that address specific risks. These standards not only verify the performance of the gloves but also help welders choose the right gloves for their specific tasks and environments.
Key Safety Standards for Welding Gloves
-
EN 3887:
This European standard evaluates a glove’s resistance to mechanical hazards, including abrasions, cuts, tears, and punctures. Welding gloves meeting EN 388 provide enhanced protection against sharp edges and other mechanical risks commonly encountered in welding environments.- Tested Parameters: Abrasion resistance, blade cut resistance, tear resistance, puncture resistance.
- Ideal For: Tasks involving handling sharp or abrasive materials alongside welding.
-
EN 4078:
Specifically focused on heat resistance, EN 407 ensures gloves provide adequate protection against various forms of thermal hazards, including radiant heat, contact heat, convective heat, and even small molten splashes. Gloves rated under EN 407 are essential for welders exposed to high temperatures or molten metal.- Tested Parameters: Resistance to flammability, radiant heat, convective heat, contact heat, and molten metal splashes.
- Ideal For: High-heat welding methods such as MIG and stick welding.
-
ANSI/ISEA 105:
This American standard outlines performance criteria for cut resistance, heat protection, and chemical resistance. Welding gloves meeting ANSI/ISEA 105 ensure superior protection against cuts and burns, making them suitable for various welding tasks that require handling sharp tools or working in high-heat conditions.- Tested Parameters: Cut resistance (levels A1-A9), heat resistance, and other workplace-specific hazards.
- Ideal For: Broad industrial applications, including welding in diverse environments.
-
NFPA 2112:
Created by the National Fire Protection Association, this standard focuses on flame-resistant garments for industrial settings. Welding gloves compliant with NFPA 2112 offer protection against flash fires and other flame-related hazards, ensuring maximum safety for workers in high-risk environments.- Tested Parameters: Flame resistance, heat transfer, and durability in fire-related scenarios.
- Ideal For: Industrial welding applications where fire risk is significant.
Certification Symbols
To verify compliance with these safety standards, always check for certification labels on the gloves. These labels indicate that the gloves have been tested and meet specific performance criteria.
- Example: A glove labeled “EN 407” will include numerical ratings for heat performance categories such as radiant heat (level 1-4), contact heat (level 1-4), and molten splash resistance (level 1-4).
Why It Matters: Certification labels provide crucial information at a glance, helping welders identify gloves that meet the demands of their tasks. Gloves without proper certifications may not offer the necessary protection, increasing the risk of injury.
Choosing Standards-Based Welding Gloves
When selecting welding gloves, consider the specific hazards you’ll encounter and match the gloves’ certifications to your needs.
- For high-heat applications, prioritize gloves with EN 407 ratings.
- If you’re working with sharp tools or materials, look for gloves certified under EN 388 or ANSI/ISEA 105.
- In environments with potential fire hazards, choose gloves that meet NFPA 2112 standards.
By ensuring compliance with these safety standards, you can confidently rely on your welding gloves to provide the protection and performance needed for even the toughest tasks.
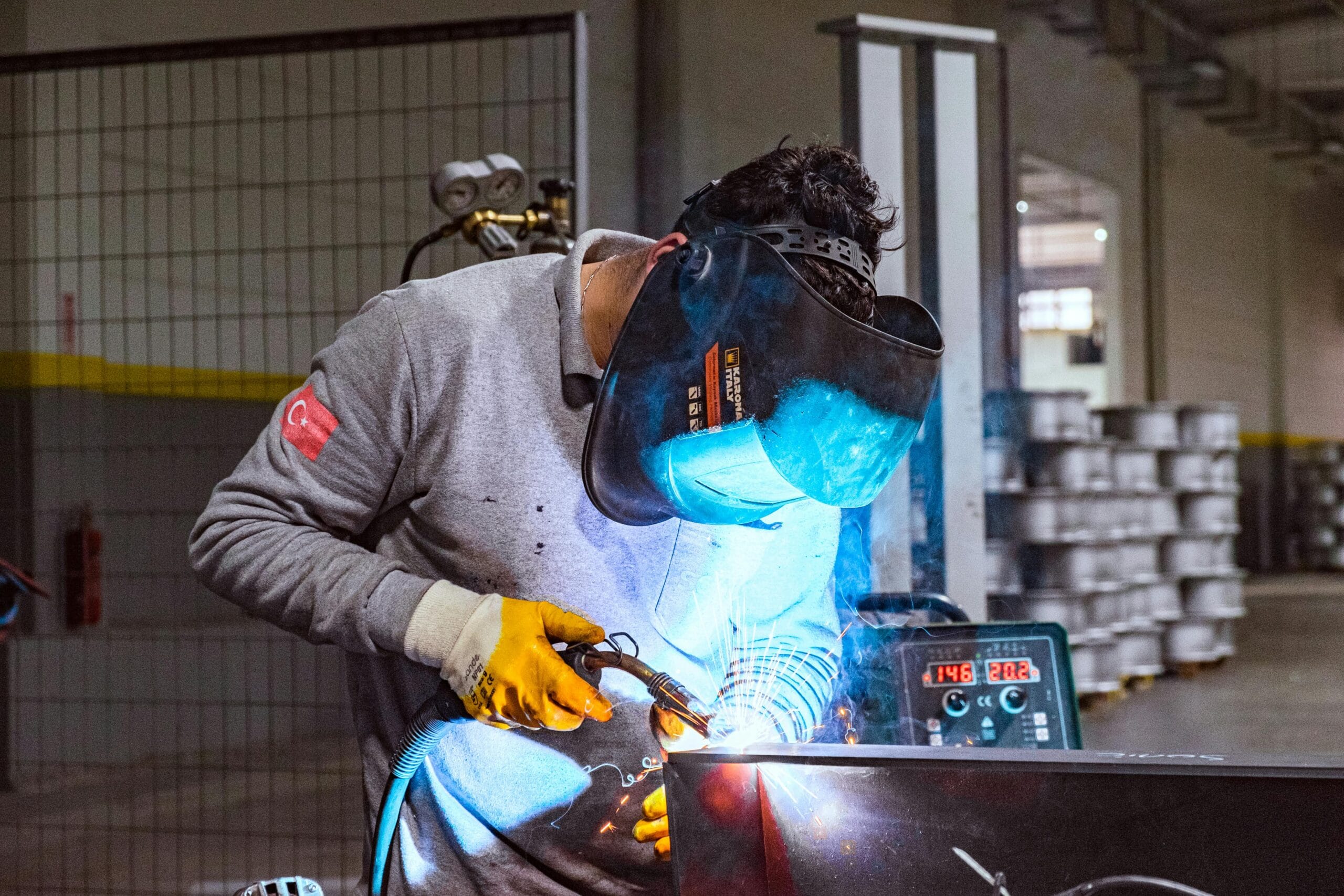

How does glove thickness affect comfort and safety during welding?
The thickness of welding gloves is a critical factor that directly influences both protection and dexterity. Selecting the right glove thickness can mean the difference between ensuring safety and maintaining precise control during welding tasks. Each thickness level offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand how glove thickness aligns with the demands of your specific welding projects.
Impact of Glove Thickness
| Thickness | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Thick Gloves | Excellent protection against high heat, durable, suitable for intense welding tasks like stick and MIG welding. | Reduced finger mobility, less precision, may lead to hand fatigue over time. |
| Thin Gloves | Enhanced dexterity for precise movements, lightweight and comfortable for extended use, ideal for TIG welding. | Limited heat resistance, less durable, and may wear out faster in high-heat environments. |
-
Thicker Gloves:
- Advantages: Thick gloves are specifically designed to handle high-heat environments where the risk of burns and sparks is significant. They provide superior protection and durability, making them an excellent choice for heavy-duty welding methods such as stick or MIG welding. The added padding also helps shield against abrasions and impacts.
- Disadvantages: While protective, their bulkiness can limit fine motor control, making tasks that require precision, such as delicate TIG welding, more challenging. Over time, the weight and stiffness of thicker gloves may also lead to hand fatigue, reducing overall productivity.
-
Thinner Gloves:
- Advantages: Thin gloves prioritize dexterity and precision, enabling welders to perform intricate tasks with ease. They are lightweight, making them comfortable for extended use, and are particularly well-suited for TIG welding, where precise control over the welding torch is essential.
- Disadvantages: The reduced thickness compromises heat resistance, leaving welders more exposed to burns in high-heat scenarios. Thinner gloves also tend to wear out faster when used in demanding conditions, leading to a shorter lifespan.
Choosing the Right Thickness for Your Welding Needs
When deciding on glove thickness, consider the specific requirements of your welding project:
- High-heat tasks: For processes like stick or MIG welding that generate intense heat and sparks, opt for thicker gloves. These provide the necessary protection to keep your hands safe while ensuring durability in challenging environments.
- Precision tasks: If your work involves detailed welding, such as TIG welding, choose thinner gloves that enhance dexterity and allow greater control over tools and materials.
Additional Tips for Selecting Glove Thickness
- Layering Options: Some welders use liner gloves beneath thicker welding gloves to improve comfort without sacrificing protection.
- Material Matters: The type of material, such as cowhide, goatskin, or deerskin, also affects how well a glove balances thickness with flexibility and durability.
- Test for Comfort: Whenever possible, try on gloves to ensure a good fit that doesn’t compromise your ability to work safely or efficiently.
By carefully evaluating your project’s heat exposure and precision requirements, you can find the ideal balance of glove thickness to enhance both safety and comfort.
Conclusion
Selecting the perfect welding gloves requires understanding your project’s demands and matching them with the appropriate materials, design, and safety standards. By considering the type of welding, heat exposure, and required dexterity, you can choose gloves that ensure safety and improve performance. Whether you’re tackling intricate TIG welding or heavy-duty stick welding, the right gloves make all the difference.
-
Linking this keyword highlights the specific benefits of goatskin, such as its lightweight and excellent grip, which are critical for precise and detailed TIG welding tasks. ↩
-
This keyword helps explain how pigskin’s durability, breathability, and resistance to wet conditions make it a reliable choice for tough welding environments. ↩
-
Linking this keyword allows users to learn about the durability, heat resistance, and flexibility of cowhide, which make it ideal for demanding tasks like MIG and stick welding. ↩
-
Linking this keyword highlights goatskin’s lightweight and abrasion-resistant qualities, which are critical for tasks requiring fine motor control and prolonged use. ↩
-
This keyword explains the role of materials like cowhide and pigskin in providing the durability and heat resistance necessary for MIG welding tasks. ↩
-
Linking this keyword highlights deerskin’s soft texture and high dexterity, crucial for tasks demanding precise hand control, such as TIG welding. ↩
-
This keyword provides detailed insights into how EN 388 certification ensures resistance to abrasions, cuts, tears, and punctures, making it essential for tasks involving sharp materials. ↩
-
Linking this keyword helps explain the importance of EN 407-rated gloves for handling extreme temperatures and molten metal splashes in welding environments. ↩
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
