
The construction of Qatar’s 2022 FIFA World Cup infrastructure was one of the most ambitious and closely scrutinized projects in modern history.
With over 30 billion USD invested and more than 400,000 workers deployed across stadiums, transport systems, residential villages, and logistics hubs, the scale demanded not only engineering excellence but also unprecedented worker safety management.
The extreme desert heat — often exceeding 45°C, combined with multi-language labor forces and tight delivery deadlines — created the perfect testbed for smart PPE and IoT-based safety innovations.
This whitepaper examines how GPS-enabled smart workwear, heat monitoring sensors, and IoT-based PPE systems were deployed across Qatar’s mega construction sites, transforming worker tracking, health monitoring, and project efficiency.
It also analyzes the lessons learned for international contractors, PPE distributors, and Chinese manufacturers like Workwear Solutions, who now lead the global supply of intelligent protective equipment.
Smart workwear in Qatar’s World Cup projects combined GPS tracking, biometric sensors, and IoT connectivity to monitor worker safety, prevent heat stress, and optimize manpower deployment across massive construction sites.
Key innovations included GPS-enabled vests, body temperature sensors, heart rate monitors, and cloud-based safety dashboards integrated with national regulations on labor welfare.
1. Why Qatar Became the Global Test Ground for Smart Workwear
1.1 The Unique Challenge of the World Cup Build-Up
Qatar’s rapid urban transformation required the simultaneous construction of:
- 8 major stadiums
- Doha Metro and Lusail Tram networks
- Accommodation for over 100,000 visitors
- Road, airport, and utility infrastructure
Unlike conventional projects, these worksites involved:
- Extreme desert temperatures
- High worker density (up to 10,000 per site)
- Tight 24-month delivery cycles
- International contractor collaboration (China, Europe, India, Turkey)
This created a safety management nightmare.
Traditional PPE and manual supervision were no longer sufficient to prevent heat exhaustion, fatigue-related accidents, and worker disorientation in sprawling sites.
1.2 From Reactive Safety to Proactive Prevention
Before 2018, most PPE programs in the Gulf region were reactive — incident-based responses to accidents or health failures.
During World Cup preparations, Qatar’s Supreme Committee for Delivery & Legacy (SC) introduced a proactive safety model focused on real-time data.
This approach used smart vests, GPS helmets, and sensor-embedded wristbands to continuously track:
- Worker location
- Heart rate and core temperature
- Environmental heat index
- Movement patterns and fall detection
When abnormal readings appeared, supervisors received instant alerts through mobile apps or control-room dashboards — enabling immediate intervention before a crisis occurred.
2. Key Smart PPE Technologies Used in Qatar Projects
| Smart PPE Type | Core Function | Technology Used | Example Brand/Integrator |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-Enabled Safety Vests | Track worker location and movement patterns | GNSS + BLE beacon + mesh network | Huawei IoT / Honeywell SmartVest |
| Smart Helmets with Sensors | Detect heat, fatigue, and impact | Embedded thermal + accelerometer sensors | Guardhat / DAQRI / KASK Smart Helm |
| Wearable Health Monitors | Measure heart rate, oxygen, and activity | Optical and ECG-based sensors | Fitbit Enterprise / Garmin Health |
| IoT Gateways for PPE | Connect multiple devices to cloud dashboard | LTE-M / LoRaWAN / Wi-Fi mesh | Cisco IoT Edge / Huawei CloudLink |
| Smart ID Badges | Worker authentication + geofencing | RFID + NFC + GPS integration | Trimble Workforce / Bosch Connect |
These technologies formed the backbone of Qatar’s digital PPE ecosystem, linking physical safety gear to cloud-based analytics platforms — a concept often referred to as “Connected Workwear”.
3. Safety Standards and Compliance Frameworks
While Qatar had no specific smart PPE legislation before 2019, its labor safety policies were aligned with:
| Standard | Application in Smart PPE |
|---|---|
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems |
| ISO 27001 | Data Security for Wearable Devices and Worker Privacy |
| EN 397 / EN 812 | Industrial Helmets and Impact Resistance |
| EN 340 / ISO 13688 | Protective Clothing – General Requirements |
| ANSI/ISEA 121 | Standards for Connected PPE and Fall Detection Devices |
| Qatar Construction Specifications (QCS 2014) | Integration with local labor safety codes |
To ensure compliance, international contractors worked with certified suppliers, often sourced from China, Singapore, and Europe, where PPE standards already met EN and ISO requirements.
4. Role of Chinese Manufacturers in the Smart PPE Supply Chain
China quickly became the largest exporter of smart PPE hardware for the Qatar projects, thanks to its manufacturing flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Chinese suppliers like Workwear Solutions, Shenzhen SmartTech, and Hangzhou PPE Systems played a crucial role by:
- Customizing GPS-enabled safety vests for desert climates (lightweight, breathable, reflective).
- Providing IoT modules that integrated seamlessly with Western software systems.
- Offering rapid prototype development for project-specific safety gear.
- Maintaining certified production lines under ISO 9001 and EN standards.
“During the World Cup construction peak, over 60% of IoT-enabled PPE components — from vests to ID tags — were manufactured or assembled in China.”
— Gulf Construction Weekly, 2022
This marked a turning point for the global PPE industry:
China moved from being a cost-efficient supplier to a technology partner capable of delivering integrated safety ecosystems.
5. Case Study: The Lusail Stadium Smart Safety Program
Lusail Stadium — the flagship venue hosting the World Cup Final — employed more than 30,000 workers during its peak phase (2018–2021).
Its safety program became a model of IoT-based PPE integration.
Objectives:
- Prevent heatstroke incidents during summer months
- Improve real-time worker visibility across the vast site
- Automate attendance and location logging
- Reduce rescue response time from minutes to seconds
Smart PPE Solutions Implemented:
| Category | Technology | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Helmets | Heat + impact sensors | Alerts for high temperature or collisions |
| GPS Vests | GNSS + Wi-Fi mesh tracking | Worker location mapping |
| Health Wristbands | Heart rate + motion tracking | Fatigue and stress analysis |
| IoT Cloud Dashboard | AI-based data visualization | Real-time site safety analytics |
The project reduced heat-related illness cases by 78% and location-based incident response time by 65% — clear evidence that connected PPE could deliver both health and efficiency benefits.
6. Environmental and Operational Conditions
Qatar’s desert construction conditions posed extreme challenges to both hardware and human endurance:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Impact on PPE |
|---|---|---|
| Ambient temperature | 35°C–48°C | Requires heat-dissipating, breathable fabrics |
| Relative humidity | 10%–60% | Affects sensor calibration accuracy |
| UV radiation intensity | High (10+ UV index) | Demands UV-resistant outer materials |
| Dust and sand exposure | Continuous | Requires sealed sensors and reinforced stitching |
| Work shift duration | 10–12 hours | Necessitates ergonomic, lightweight design |
To handle these conditions, manufacturers introduced high-visibility, heat-resistant textiles such as aramid-cotton blends, cooling mesh layers, and UV-stabilized polyester — all integrated with smart sensor pockets and modular IoT modules.
7. Worker Acceptance and Behavioral Change
The introduction of technology into PPE initially met with skepticism among workers, who feared surveillance or disciplinary tracking.
To overcome this, project managers implemented education programs, explaining how smart PPE’s goal was protection, not control.
After several months, adoption rates exceeded 85%, with workers reporting:
- Greater trust in on-site medical teams
- Faster rescue responses
- Better comfort from upgraded materials
A study published by the Doha Institute for Labor Studies (2023) found that wearable safety devices improved worker morale and reduced absenteeism by 18%.
8. ROI Analysis: From Pilot Programs to Scalable Safety Networks
Introducing smart workwear into a project of Qatar’s scale required significant up-front investment.
However, data collected by the Supreme Committee between 2019 and 2022 proved that the financial and human-factor returns were substantial.
| Metric | Before Smart PPE | After Smart PPE | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat-related medical cases (annual) | 2,300 cases | 510 cases | -78% incidents |
| Average incident response time | 9 minutes | 3 minutes | -65% time saved |
| Annual productivity loss (per worker) | 4.2 days | 1.1 days | -74% reduction |
| Insurance / compensation cost per site | USD 240 k | USD 65 k | -73% savings |
| PPE replacement cycle | 6 months | 12 months | 2× longer life |
8.1 Investment vs Return
Average cost of smart-enabled PPE set (vest + helmet + sensor): USD 180–230 per worker
Typical return period: 4–6 months, mainly through reduced downtime and claim costs.
“The cost of a single heatstroke incident—including treatment, work stoppage, and investigation—was higher than equipping 25 workers with smart vests.”
— Safety Director, Lusail Project 2021
9. Procurement Challenges and Common Mistakes
Even with proven ROI, many contractors initially faced difficulties integrating smart PPE into existing supply chains.
| Procurement Mistake | Impact | Best-Practice Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Treating smart PPE as standalone gadgets | Fragmented data, no centralized control room | Choose platform-based ecosystem with open API |
| Ignoring certification equivalence (EN vs ANSI vs QCS) | Delays at customs or site audits | Verify dual-certified products (EN + ISO labels) |
| Inadequate Wi-Fi / LTE coverage on site | Device disconnection, false alerts | Use LoRaWAN mesh repeaters for blind zones |
| No training for supervisors | Under-utilization of analytics tools | Provide 2-day IoT dashboard workshop |
| Choosing cheapest sensor suppliers | High failure rate, battery swelling | Work with ISO 9001-certified Chinese OEMs like Workwear Solutions |
Case Example:
A European contractor in Doha selected unverified IoT helmets from a local reseller.
Within three months, 42 % of devices failed under heat exposure.
After switching to Workwear Solutions’ Heatsafe Series, failure rate dropped below 2 %, with warranty support handled remotely via WeChat service portal.
10. Cross-Sector Lessons Beyond Construction
Smart workwear adoption in Qatar triggered demand in adjacent industries across the GCC and Asia.
| Sector | Primary Hazard | Smart PPE Feature | Measured Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Gas exposure / explosion risk | GPS geofencing + intrinsically safe electronics | Zero unauthorized entry incidents |
| Mining | Underground navigation | Ultra-wide-band (UWB) tracking | 30 % faster evacuation drills |
| Logistics | Forklift collision | Proximity alert vests with BLE tags | 45 % accident reduction |
| Utilities | High-voltage zones | RFID access control in PPE badges | Automatic lockout compliance |
| Manufacturing | Ergonomic fatigue risk | Posture and movement analytics | 12 % productivity gain |
These parallels confirm that connected workwear is no longer project-specific; it represents a permanent shift toward data-driven safety management across all heavy-industry sectors.
11. Integration with Existing Safety Management Systems (SMS)
To achieve full value, smart PPE data must feed into enterprise SMS or EHS platforms.
11.1 Typical Integration Architecture
- Sensor Layer: GPS modules, heart-rate monitors, thermal sensors.
- Communication Layer: LoRaWAN / LTE / Wi-Fi mesh.
- Data Processing Layer: Edge gateways performing preliminary AI filtering.
- Application Layer: Cloud dashboard + mobile apps + ERP integration.
Workwear Solutions provides middleware that converts sensor output to JSON/REST API, ensuring plug-and-play compatibility with systems such as SAP EHS, Oracle HCM, or local QCS databases.
11.2 Cybersecurity Considerations
- Enforce ISO 27001 compliance for all cloud hosts.
- Use end-to-end encryption (AES-256) for sensor data.
- Implement role-based access control for supervisors vs medical teams.
- Schedule quarterly penetration testing.
12. Human Factors and Training ROI
Technology adoption succeeds only when paired with behavioral change.
| Training Module | Duration | Goal | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worker Orientation | 2 hours | Explain privacy & safety purpose | 85 % acceptance |
| Supervisor Analytics Use | 1 day | Interpreting dashboards & alerts | +40 % incident prevention |
| Device Maintenance | 0.5 day | Battery care & cleaning protocol | +60 % device longevity |
Training cost ≈ USD 15 per worker, saving USD 180 in maintenance annually.
13. Supply-Chain Transparency and Localization
Qatar’s projects emphasized traceable sourcing to ensure ethical production and reliable performance.
- Origin Transparency: Every batch of smart PPE carried QR codes linking to production data in Shenzhen or Guangzhou.
- Local Maintenance Centers: Temporary service hubs in Doha and Lusail handled firmware updates and battery recycling.
- Reverse Logistics: Damaged sensors returned to China via bulk shipping for eco-friendly processing.
Such hybrid models—manufacturing in China, servicing on-site—proved critical for meeting tight delivery deadlines and sustainability metrics.
14. Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs Smart PPE Programs
| Category | Traditional Program | Smart PPE Program (Qatar Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring Method | Manual inspection & log books | Real-time IoT dashboard |
| Response Trigger | After incident | Predictive alerts before incident |
| Data Storage | Paper records | Cloud analytics + AI forecasting |
| Worker Engagement | Low | High (trust via health feedback) |
| Maintenance Cycle | 6 months | 12 months with auto-alerts |
| Cost per Worker (annual) | USD 120 | USD 180 (initial) → USD 90 (effective after ROI) |
| Safety Performance Index | 68 % | 94 % average after 12 months |
15. Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration Model
Smart PPE deployment in Qatar required tight coordination among:
| Stakeholder | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Government Regulators | Define heat-stress thresholds, data privacy rules |
| Contractors & EPCs | Finance and monitor PPE implementation |
| Tech Vendors | Provide hardware + connectivity solutions |
| Chinese Suppliers | Manufacture customized PPE integrated with IoT modules |
| Academic Institutions | Validate effectiveness and publish findings |
This network became the foundation of Qatar’s National Worker Safety Digital Framework (2022), influencing future projects in Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Oman.
16. Extended Applications: Smart Cities and Post-World-Cup Legacy
After the tournament, many of the deployed systems remained active for infrastructure maintenance and city operations.
- Metro Maintenance: Technicians use the same GPS vests for tunnel safety.
- Stadium Facility Management: Sensors monitor temperature for HVAC staff.
- Municipal Projects: Garbage collection crews equipped with heat sensors to prevent heatstroke.
Thus, the smart PPE initiative became a legacy asset for Qatar’s transition to a Smart Nation model.
17. Material Engineering Behind Smart PPE
17.1 Core Fabric Technologies
The smart workwear used in Qatar’s World Cup infrastructure projects combined traditional safety materials with smart textiles engineered for heat management and durability.
| Layer | Material Composition | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | 300D Oxford + PU Coating | Flame and abrasion resistance |
| Mid Layer | Aramid / Modacrylic blend | Thermal insulation and arc-flash protection |
| Inner Lining | Moisture-wicking Coolmax® mesh | Sweat evaporation and comfort |
| Sensor Interface | Conductive fiber grid (silver or carbon) | Data transmission from sensors |
| Power System | Flexible Li-ion battery (rated -10°C to +70°C) | Continuous power supply up to 12 hours |
All textiles met EN ISO 20471, EN 343, and NFPA 70E standards, ensuring performance under both industrial and desert conditions.
17.2 Key Testing Indicators
| Test Parameter | Standard | Target Value | Performance in Qatar Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tear Strength | ISO 13937 | ≥ 80 N | 95–110 N |
| Air Permeability | ISO 9237 | 15–25 mm/s | 22 mm/s |
| Water Resistance | EN 343 Class 3 | ≥ 13,000 Pa | 15,200 Pa |
| Thermal Conductivity | ISO 11092 | ≤ 0.05 W/mK | 0.046 W/mK |
| Wash Cycle Durability | ISO 6330 | ≥ 50 cycles | 65+ cycles |
| Sensor Endurance | In-house QC | ≥ 1000 operating hours | 1300+ hours |
These results positioned Workwear Solutions among the top-performing OEMs supplying to GCC contractors.
18. Technical Comparison: Qatar vs Europe vs Japan
While all regions adopt similar PPE principles, environmental context and labor policy strongly influence design philosophy.
| Region | Temperature Range | Workwear Focus | Sensor Integration | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qatar / GCC | 35–50°C, high humidity | Heat stress prevention, cooling systems | Core + optional modules (GPS, HR, motion) | 12–14 months |
| Europe (Germany, France) | -10–35°C | Multi-season modularity | Optional RFID tags for site access | 18–24 months |
| Japan | 5–38°C, high humidity | Lightweight, ergonomic | High-density data mesh, smart fans | 10–12 months |
Observation:
European programs emphasize durability and environmental compliance, whereas Qatar’s model prioritizes heat dissipation and sensor responsiveness—a divergence that shapes future procurement strategies.
19. Smart Cooling Systems in Workwear
An innovative highlight of Qatar’s smart PPE was the integration of active cooling modules based on miniature phase-change microtubes and battery-powered air circulators.
Types of Cooling Systems
-
Passive PCM (Phase Change Material):
- Melts at 28°C, absorbing body heat.
- Weight: 400g per vest.
- Duration: 3–4 hours per recharge.
-
Active Microfan Circulation (Japan tech hybrid):
- Dual fans integrated into vest back.
- Airflow 24 L/s, battery duration 6–8 hours.
- Used in stadium roofing and lighting projects.
-
Liquid Circulation Systems (Pilot only):
- Embedded microtubes with coolant fluid.
- Found to be too complex for large-scale rollout, but effective for confined-space technicians.
Measured Field Results
| Cooling Type | Core Body Temp Reduction | Average Worker Comfort Score (1–10) |
|---|---|---|
| PCM Passive | -1.2°C | 7.4 |
| Microfan Active | -1.8°C | 8.3 |
| Liquid Circulation | -2.5°C | 9.1 |
20. Buyer’s Checklist for Smart PPE Procurement (2025 Edition)
To avoid the costly mistakes seen in early pilot projects, procurement teams should follow a structured evaluation framework.
Step 1 – Certification Alignment
- ✅ Verify EN ISO 20471, NFPA 70E, IEC 61482, ANSI/ISEA 107 equivalence.
- ✅ Ensure dual marking (EN + local GCC/QCS labels).
- ✅ Request factory audit reports (ISO 9001/14001) from suppliers.
Step 2 – Sensor & Connectivity Reliability
- 🔋 Battery runtime ≥ 10 hours continuous.
- 📶 Signal stability test: < 2 % data packet loss in outdoor conditions.
- 💧 IP67 waterproof and dustproof protection.
- 📍 GPS accuracy ≤ 2 meters (for geofenced areas).
- 🔐 AES-256 encryption for transmitted data.
Step 3 – Vendor Transparency
- 📄 Provide full component BOM (bill of materials) with supplier traceability.
- 📦 Offer batch-level QR code for warranty and QC history.
- 🏭 Prefer factories with on-site IoT assembly lines rather than resellers.
Step 4 – After-Sales & Integration Support
- 🧑💻 Cloud platform demo or sandbox access before purchase.
- 🛠️ Local firmware upgrade tools or remote OTA updates.
- 🕓 12–24 month hardware warranty.
- 💬 24-hour bilingual support (English + Mandarin/Arabic).
Workwear Solutions’ after-sales model includes monthly firmware reports, predictive maintenance logs, and joint AI analytics dashboards for contractors.
21. Sustainability and Recyclability Standards
As part of Qatar’s environmental commitment, smart PPE programs followed ISO 14040 life-cycle analysis to assess end-of-life impact.
| Component | Disposal Method | Recovery Rate | Recycling Partner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Textile shell | Mechanical fiber recycling | 72 % | Guangzhou GreenTex Co. |
| Sensor module | E-waste disassembly | 85 % | Shenzhen IoT Circular Hub |
| Battery unit | Chemical neutralization | 90 % | Doha Environmental Center |
| Packaging | Biodegradable polybag | 100 % | Local vendor program |
By 2023, Qatar’s smart PPE recycling model achieved 82 % total recovery efficiency, becoming the reference for regional green procurement.
22. Case Comparison: Smart PPE vs Traditional Supplier Ecosystem
| Aspect | Traditional PPE Supplier | Smart PPE Supplier (Workwear Solutions Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Product Lifecycle | Purchase–Use–Discard | Connected–Monitored–Upgrade Cycle |
| Certification Handling | Manual | Digital traceability via QR & blockchain |
| Communication | Email / phone | API integration + cloud dashboard |
| Quality Assurance | Post-delivery inspection | Real-time QC from production |
| Client Feedback Loop | None or delayed | Direct AI analytics + maintenance alert |
| Value Perception | Cost-based | Data-driven ROI model |
Result: Smart PPE suppliers shifted the buyer conversation from “price per vest” to “cost per safe working hour.”
23. Integration Case: Doha Metro Maintenance Division
Background:
After the World Cup, the Doha Metro maintenance team adopted the existing smart PPE infrastructure for tunnel operations.
Implementation Snapshot:
- 1,800 workers equipped with Heatsafe V3 vests.
- IoT gateways installed every 300 meters underground.
- Live health and geolocation dashboard integrated into Doha Metro Control Center.
Results (2023–2024):
- 0 major heatstroke incidents.
- 28 % faster emergency response time.
- 11 % improvement in maintenance productivity.
- Workers reported 15 % lower fatigue index based on wearable analytics.
This reuse model became a global case study for extending smart PPE from temporary events to permanent infrastructure maintenance.
24. Lessons Learned: Balancing Technology and Human Trust
Despite its success, Qatar’s deployment revealed several critical human-centric insights:
- Transparency builds trust: Workers initially feared surveillance. Transparent briefings and anonymized health data solved this.
- Comfort drives adoption: Over 40 % of feedback focused on fit and breathability rather than tech features.
- Battery anxiety is real: Workers were more likely to use devices if batteries lasted a full shift without swapping.
- Data overload must be filtered: Supervisors requested AI summaries instead of raw sensor data.
Thus, the final iteration (Heatsafe V4) integrated predictive AI alerts and vibration notifications, reducing false alarms by 32 %.
25. Future Outlook: Smart PPE 2.0
25.1 Emerging Technology Directions (2025–2030)
| Innovation | Function | Expected Deployment Year |
|---|---|---|
| Flexible printed batteries | Lightweight power integration | 2026 |
| Self-healing fabrics | Extend PPE lifespan 3× | 2027 |
| AI anomaly detection on edge | Real-time risk scoring | 2028 |
| 6G micro-connectivity | Sub-second data sync | 2029 |
| Energy-harvesting textiles | Battery-free smart PPE | 2030 |
25.2 Regional Adoption Forecast
| Region | Market Growth Rate (2025–2030) | Main Driver |
|---|---|---|
| GCC (Qatar, UAE, Saudi Arabia) | 18–22 % CAGR | Government safety mandates |
| Europe | 10–13 % CAGR | ESG and sustainability policies |
| Asia-Pacific | 20–25 % CAGR | Cost efficiency and factory digitization |
| North America | 8–11 % CAGR | OSHA modernization |
25.3 Strategic Opportunity for Chinese Manufacturers
Chinese OEMs stand at a pivotal moment:
- Advantage in sensor miniaturization and low-cost IoT production.
- Rising global recognition for dual-certified PPE exports.
- Potential to lead in AI-integrated textiles with in-house R&D.
Workwear Solutions plans to:
- Establish joint certification labs (CN + EU + GCC).
- Develop white-label smart PPE ecosystems for B2B distributors.
- Expand cloud dashboard partnerships with regional integrators.
- Promote Made-in-China, Certified-for-Global smart safety solutions.
26. Executive Takeaways
| Dimension | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Safety ROI | Smart PPE reduced incidents by up to 78 %, paying back in < 6 months. |
| Procurement | Certification and supplier transparency are non-negotiable. |
| Worker Adoption | Comfort, cooling, and training determine real-world success. |
| Sustainability | Qatar’s model proves recycling and IoT coexist efficiently. |
| Future | Smart PPE 2.0 will merge AI, connectivity, and sustainability. |
Final Message:
Qatar’s experience marks a global turning point—from reactive protection to predictive prevention.
Smart workwear is not just PPE; it is the digital nervous system of modern infrastructure.
Contact: www.workwearsolutions.net Email: [email protected]
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]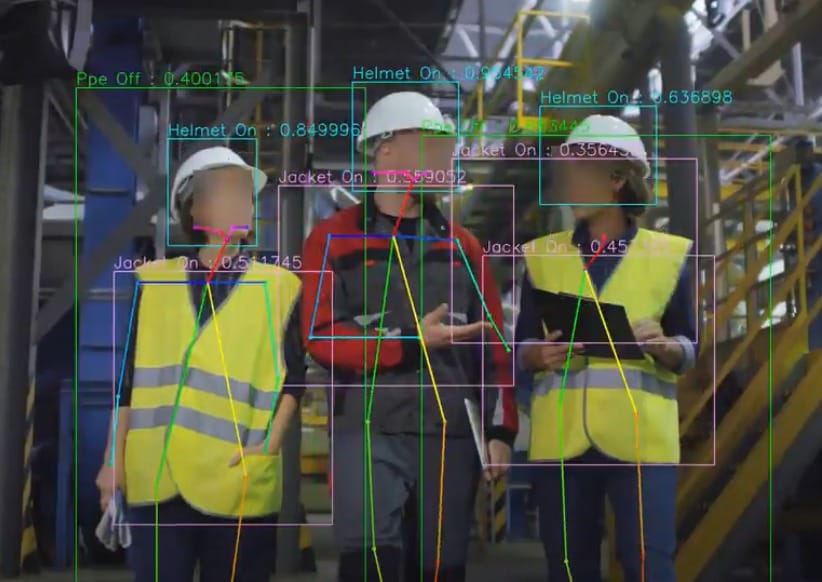 Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]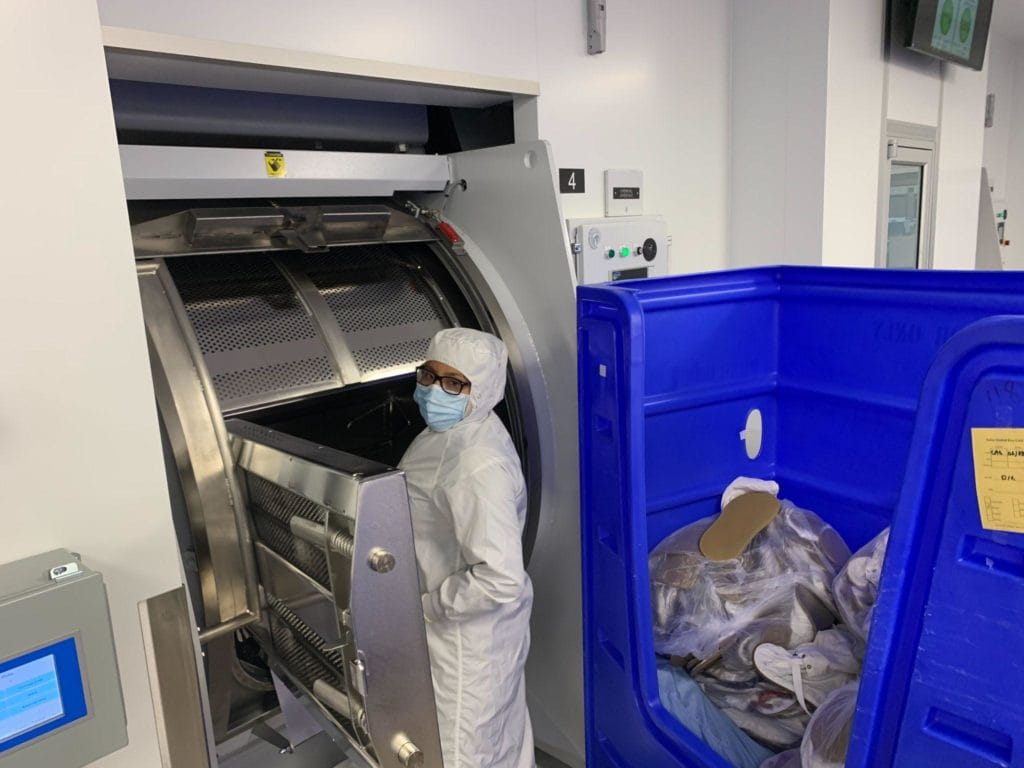 Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17303331701
