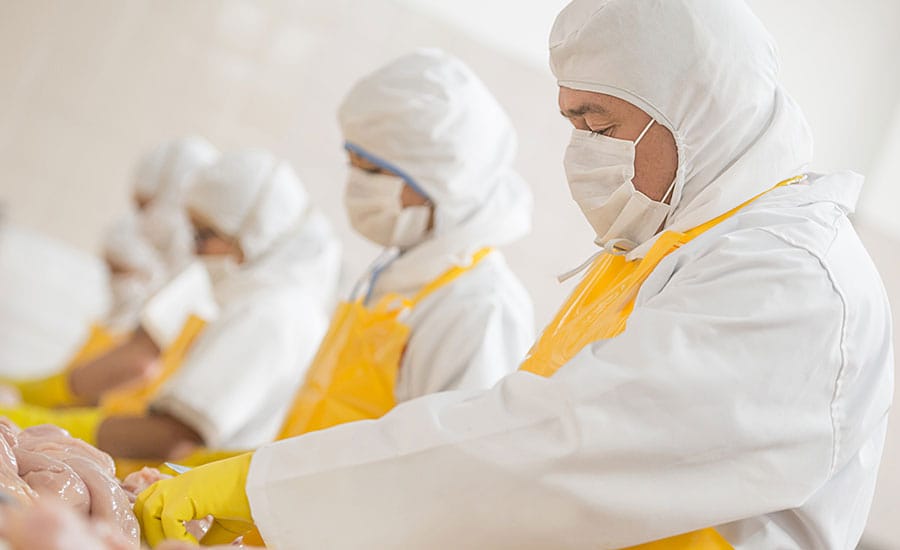

Industrial workwear is no longer evaluated solely on strength and protection. In modern factories, logistics hubs, and food processing plants, cleanliness, maintenance efficiency, and lifecycle cost have become equally critical performance indicators.
Nano-coatings—ultra-thin surface treatments engineered at the nanometer scale—are rapidly reshaping how workwear performs in dirty, high-contact, and hygiene-sensitive environments. By delivering anti-stain, liquid-repellent, and soil-release properties, nano-coated workwear can reduce washing frequency by approximately 30–50%, without compromising comfort or safety.
This has profound implications for food factories, where hygiene and appearance are tightly regulated, and for logistics operations, where garments are exposed to dust, oil, rain, and repeated handling.
This guide follows the exact analytical structure of the dairy PPE article, combining:
- Technical fundamentals
- Standards and compliance logic
- Material and coating comparisons
- Industry-specific case scenarios
- Procurement mistakes and ROI modeling
- Buyer checklists and advanced sourcing strategies
The result is a complete decision-making framework for adopting nano-coated workwear at scale.
Google Snippet: Quick Answer
Nano-coatings on workwear create invisible, durable barriers that repel liquids, oils, and dirt, significantly reducing staining and odor buildup.
By keeping garments cleaner for longer, they reduce washing frequency by 30–50%, lower water and energy consumption, and extend garment lifespan. Nano-coated workwear is especially suitable for food processing plants and logistics operations, where hygiene, appearance, and efficiency are critical.
1. Why Modern Workwear Needs Reduced Washing Frequency
Frequent washing has traditionally been treated as a necessary cost of industrial hygiene. In reality, it is one of the largest hidden cost drivers in workwear programs.
1.1 The Real Cost of Frequent Washing
Every wash cycle contributes to:
- Fabric fiber degradation
- Color fading and loss of professional appearance
- Shrinkage and fit inconsistency
- Increased labor and utility costs
- Higher carbon and water footprint
In large-scale operations, laundering can account for 40–60% of total garment lifecycle cost.
Nano-coatings attack this problem at the source—not by cleaning better, but by preventing dirt from bonding to the fabric in the first place.
1.2 Why Food & Logistics Industries Are Especially Affected
Food Processing
- Strict hygiene requirements
- High exposure to liquids, fats, sauces, and proteins
- Visual cleanliness directly tied to audit outcomes
Logistics & Warehousing
- Dust, grease, rain, and handling marks
- Frequent outdoor–indoor transitions
- High garment rotation rates due to appearance degradation
For both industries, clean-looking garments are as important as protective ones.
2. What Are Nano-Coatings in Workwear?
Nano-coatings are functional surface treatments applied at the nanometer scale—thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
2.1 Core Definition
A nano-coated fabric features:
- An ultra-thin protective layer
- Chemically bonded to fiber surfaces
- Invisible and breathable
- Durable through repeated wear and washing
Unlike traditional coatings, nano-coatings:
- Do not block fabric pores
- Do not significantly alter hand feel
- Do not add noticeable weight or stiffness
2.2 What Nano-Coatings Actually Do
Depending on formulation, nano-coatings can provide:
- Hydrophobicity (water repellency)
- Oleophobicity (oil repellency)
- Anti-soiling behavior
- Easy-clean / soil-release effects
- Reduced odor absorption
These properties directly translate into less frequent washing.
3. How Nano-Coatings Work: The Science Explained Simply
Nano-coatings function by modifying surface energy at the fiber level.
3.1 Surface Energy Reduction
Dirt and liquids adhere when surface energy allows bonding. Nano-coatings:
- Lower surface energy
- Prevent liquids from spreading
- Cause contaminants to bead and roll off
This is similar to the “lotus leaf effect” observed in nature.
3.2 Fiber-Level Protection (Not a Film)
Unlike PU or PVC coatings:
- Nano-coatings do not form a continuous film
- Each fiber is individually treated
- Breathability and flexibility are preserved
This is why nano-coated garments remain comfortable even in warm environments.
3.3 Durability Through Chemical Bonding
High-quality nano-coatings:
- Chemically bond to textile fibers
- Survive 50–100 industrial wash cycles
- Maintain performance without reapplication
4. Relevant Standards and Compliance for Nano-Coated Workwear
Nano-coatings must meet both performance and regulatory safety requirements, especially in food-related environments.
| Area | Relevant Standard / Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Food Contact Safety | FDA, EU food-contact compliance | Prevent harmful migration |
| Chemical Safety | REACH, OEKO-TEX® | Worker and consumer safety |
| Wash Durability | ISO 6330 | Performance after laundering |
| Water Repellency | ISO 4920 / AATCC 22 | Spray resistance |
| Oil Repellency | AATCC 118 | Resistance to oily contaminants |
5. Material Selection: Fabrics That Benefit Most from Nano-Coatings
Nano-coatings are not equally effective on all materials.
| Base Fabric | Nano-Coating Benefit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Polyester | Excellent | Smooth fiber surface enhances effect |
| Poly/Cotton Blends | Very Good | Balance of comfort and repellency |
| Pure Cotton | Moderate | Requires optimized formulations |
| High-Visibility Fabrics | Excellent | Maintains brightness and color |
| Softshell Fabrics | Very High | Enhances weather resistance |
6. Case Study Comparisons by Industry Segment
6.1 Food Processing Plants
| Scenario | Without Nano-Coating | With Nano-Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Sauce splashes | Immediate staining | Liquids bead off |
| Visual cleanliness | 1 shift | 2–3 shifts |
| Washing frequency | Daily | Every 2–3 days |
| Audit appearance | High risk | Consistently clean |
Result:
Up to 40% reduction in washing cycles, improved audit confidence.
6.2 Logistics & Warehousing
| Scenario | Traditional Workwear | Nano-Coated Workwear |
|---|---|---|
| Dust exposure | Fibers trap particles | Dust shakes off |
| Rain exposure | Fabric absorbs moisture | Water beads and runs off |
| Appearance lifespan | 3–6 months | 9–12 months |
| Replacement rate | High | Significantly reduced |
Result:
Lower garment turnover and improved brand image.
7. Common Procurement Mistakes with Nano-Coated Workwear
| Mistake | Impact | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|---|
| Confusing nano-coating with thick coatings | Reduced comfort | Request breathability data |
| Ignoring wash durability | Performance loss | Demand ISO wash test reports |
| Overpaying for unnecessary features | Low ROI | Match coating to real contaminants |
| No field testing | User resistance | Run 30-day pilot programs |
8. ROI Analysis: Reduced Washing = Real Savings
8.1 Cost Comparison (Per 100 Workers / Year)
| Cost Category | Standard Workwear | Nano-Coated Workwear |
|---|---|---|
| Washing cycles | 18,000 | 10,800 |
| Water & energy | $22,000 | $13,200 |
| Labor | $15,000 | $9,000 |
| Garment replacement | $30,000 | $18,000 |
| Total Annual Cost | $67,000 | $40,200 |
Annual Savings: ≈ 40%
8.2 Environmental ROI
- Water usage ↓ 30–50%
- Energy consumption ↓ significantly
- Lower detergent discharge
- Reduced textile waste
This aligns strongly with ESG and sustainability targets.
9. Buyer Checklist for Nano-Coated Workwear
- [ ] Confirm food-contact or chemical safety compliance
- [ ] Verify wash durability (≥50 cycles)
- [ ] Test liquid and oil repellency
- [ ] Evaluate breathability and comfort
- [ ] Conduct real-use trials
- [ ] Calculate laundry cost reduction
- [ ] Align with sustainability goals
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Does nano-coating make fabric stiff?
A: No. High-quality nano-coatings are invisible and preserve softness.
Q2: Will repellency disappear after washing?
A: Certified coatings maintain performance through dozens of industrial wash cycles.
Q3: Is nano-coated workwear safe for food environments?
A: Yes, when compliant with FDA and EU food-contact regulations.
Q4: Can nano-coatings replace waterproof garments?
A: No. They repel liquids but do not provide full waterproof barriers.
Q5: Is the cost justified?
A: Yes—laundry and replacement savings often exceed the premium.
11. Advanced Sourcing Strategies for Nano-Coated Workwear
-
Start with High-Laundry Zones
Target roles with the highest washing frequency first. -
Request Performance Guarantees
Specify minimum wash-cycle durability. -
Pilot Before Scaling
30–60 day trials reveal real savings. -
Combine with Color Retention Fabrics
Maximize appearance lifespan. -
Integrate with Rental Programs
Laundry savings compound even faster.
12. Conclusion
Nano-coatings fundamentally change the economics of industrial workwear.
By preventing dirt and liquids from bonding to fabric, they:
- Reduce washing frequency by 30–50%
- Extend garment lifespan
- Lower water, energy, and labor costs
- Improve hygiene and professional appearance
For food factories and logistics operations, nano-coated workwear is no longer a premium novelty—it is a strategic efficiency upgrade.
📩 Looking to source nano-coated workwear solutions for food or logistics industries?
Email: [email protected]
🌐 www.workwearsolutions.net
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17303331701
