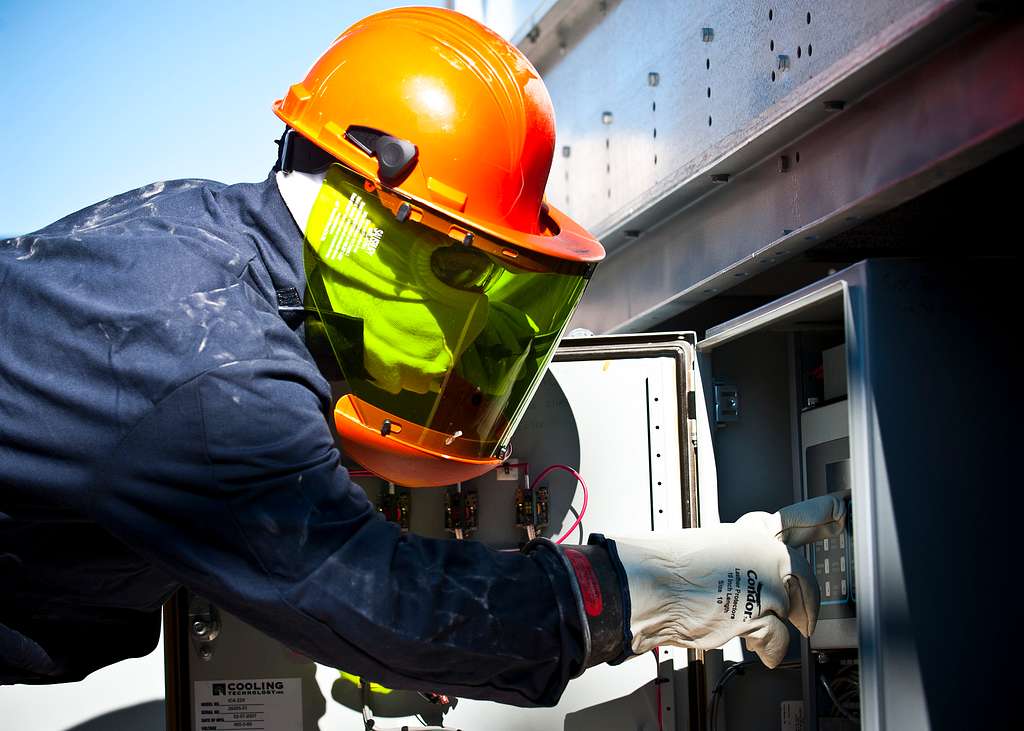

Electricity is silent but deadly. Every year, hundreds of workers suffer life-altering injuries—or worse—from arc flash incidents. And most of these tragedies could have been prevented with the right PPE. That’s where arc flash suits come in—designed not just to protect, but to save lives in some of the most dangerous work environments on earth.
An arc flash suit is a critical line of defense for electricians and maintenance teams working around high-voltage equipment. If you’re sourcing PPE for electrical safety, understanding arc flash protection is not optional—it’s essential.
What Is an Arc Flash and Why Is It Dangerous?
An arc flash is a sudden, explosive release of electrical energy caused by a fault in a high-voltage system. It creates intense heat, light, pressure, and sound—often hotter than the surface of the sun.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Temperatures can reach 35,000°F (19,400°C)
- Pressure waves can cause hearing loss or concussions
- Shrapnel from molten metal or components can lead to severe injuries or death
- Skin burns can occur even several feet from the arc
Even a brief arc event lasting milliseconds can result in catastrophic injury if workers aren’t properly protected. That’s why arc-rated PPE is a critical investment—not a nice-to-have.
What Is an Arc Flash Suit?
An arc flash suit is a specialized personal protective equipment (PPE) system designed to protect workers from the intense thermal, radiant, and physical energy generated during an arc blast.
It’s not just clothing—it’s a barrier.
Arc flash suits are:
- Made of flame-resistant (FR) materials that won’t ignite, melt, or continue burning
- Tested to withstand specific energy exposures, measured in calories/cm²
- Designed to minimize burn injury, reduce shock risk, and allow workers to evacuate safely after an incident
They’re worn in environments where standard FR clothing simply isn’t enough.
Key Components of an Arc Flash Suit
A complete arc flash suit includes multiple layers of protection, often worn together as a system. Each component plays a role in shielding different parts of the body.
Standard components include:
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Arc-rated Hood or Helmet | Protects face, head, and neck from thermal and blast injury |
| Face Shield (with anti-fog coating) | Blocks radiant heat and flying particles |
| Insulated Rubber Gloves (with leather protectors) | Prevents electrical contact injuries |
| Flame-Resistant Jacket & Pants (or Coveralls) | Core thermal protection for torso and limbs |
| Safety Boots (EH-rated) | Prevents electrical grounding through the feet |
| Optional: Balaclava, Hearing Protection | Adds protection from heat and sound shockwave |
Each piece should be ATPV-rated and used together to ensure full-body protection.
Standards and Ratings: Understanding ATPV and NFPA 70E
When it comes to arc flash suits, certification matters. You need to be sure the suit is tested, rated, and fully compliant with international standards.
Key standards to know:
- NFPA 70E: U.S. standard for electrical safety in the workplace
- ASTM F1506: Specifies performance requirements for flame-resistant fabric
- IEC 61482: International standard for arc-rated clothing
- CSA Z462: Canadian equivalent of NFPA 70E
What is ATPV?
- Stands for Arc Thermal Performance Value
- Measured in calories/cm²
- Indicates how much incident energy the fabric can absorb before the wearer would suffer second-degree burns
Example: An ATPV of 12 cal/cm² means the fabric can protect against an arc exposure of 12 calories per square centimeter. The higher the number, the greater the protection.
✅ Note for buyers: Never guess—always confirm ATPV ratings and compliance documents for every suit you order.
When and Where Arc Flash Suits Are Required
Arc flash PPE is not for every task—it’s specifically required in high-risk environments where electrical fault potential is present and hazard analysis dictates PPE use.
Typical scenarios where arc flash suits are mandatory:
- Working on energized switchgear or control panels
- Operating electrical disconnects rated 240V or higher
- Entering substations, transformer rooms, or motor control centers
- Performing testing, troubleshooting, or live diagnostics
- Industrial plants, oil & gas, mining, and utilities
According to NFPA 70E, workers must wear appropriate PPE based on arc flash boundary calculations and risk categories (often referred to as PPE Category 1 through 4).
Proper Maintenance and Storage of Arc Flash Suits
A compromised suit is a useless suit. To maintain protection, arc flash gear needs to be cared for just like any other critical safety equipment.
Best practices for maintenance:
- Inspect for tears, stains, or fabric damage before each use
- Wash using mild detergents—avoid bleach, softeners, or high heat
- Dry thoroughly to prevent mildew
- Store in a clean, dry place away from sunlight or chemical exposure
- Follow manufacturer-specific care instructions
- Replace suits immediately after any incident, burn, or contamination
Pro tip: Log inspections and cleaning dates—some companies now include QR codes on suits for digital tracking.
Conclusion
Arc flash suits aren’t just another set of workwear—they are life-saving gear for professionals who face the risk of electrical explosions daily. From proper selection and certification to maintenance and training, every part of the process matters.
If you’re sourcing arc flash PPE for your team or clients, don’t settle for generic options. Go with suits that are certified, comfortable, and tailored to your voltage environment. And if you’re not sure where to start—I’m here to help.
📩 Contact: [email protected]
🌐 Visit: www.workwearsolutions.net
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
