
Engineers and architects play crucial roles on construction sites, often collaborating to ensure structural integrity and design excellence. Safety caps1, also known as helmets, serve as vital protective gear, offering head protection against falling objects, debris, and other hazards. Interestingly, these professionals often wear different safety caps for role identification2, not just for protection but also for functionality tailored to their specific tasks.
Safety caps worn by engineers and architects differ in features, materials, and colors, reflecting their unique roles and responsibilities on-site. These differences help streamline communication, improve safety, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
What do the colors of safety caps signify on a construction site?
Colors of safety caps are not just aesthetic choices—they play a critical role in ensuring on-site organization and safety.
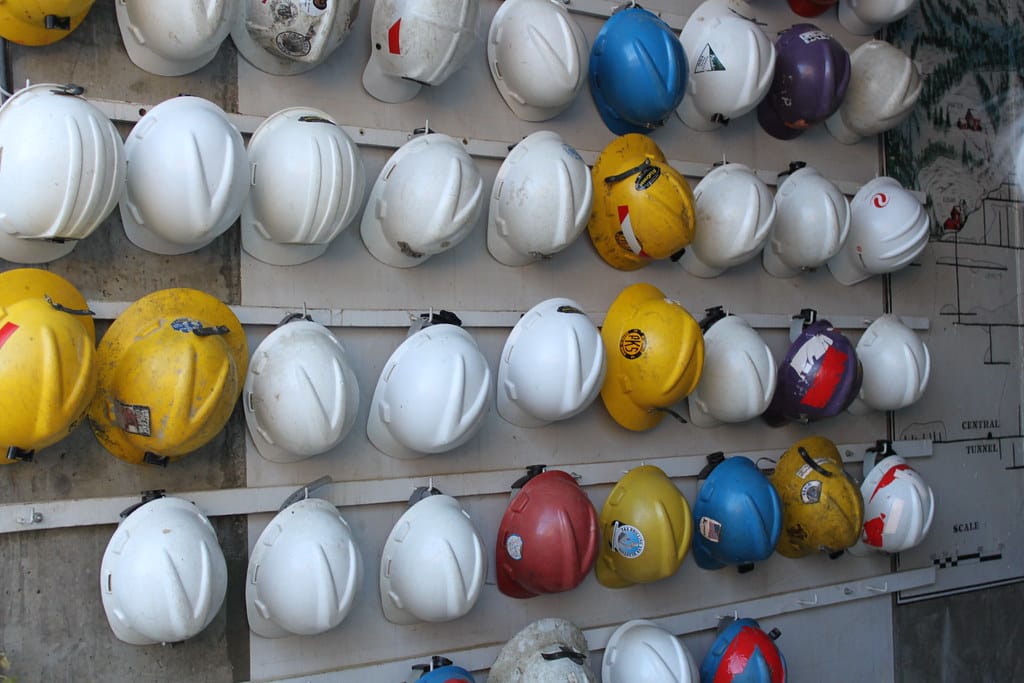
Safety cap colors3 are used to identify roles and responsibilities on a construction site, with engineers often wearing white and architects using other neutral tones like gray or black.

On a typical construction site:
- White helmets: Worn by site managers, engineers, and supervisors to denote leadership roles.
- Gray or black helmets4: Often used by architects or senior consultants during inspections.
- Blue helmets: Reserved for technical teams, such as electricians or carpenters.
- Green helmets: Designated for safety officers or environmental inspectors.
- Yellow helmets: Commonly worn by general laborers or operators.
This color coding ensures quick identification of personnel and their responsibilities, enhancing both safety and efficiency.
What are the material requirements for safety caps in high-risk industries?
Safety caps must be crafted from durable and reliable materials to protect against various hazards on-site.
High-risk industries5 demand safety caps made from impact-resistant materials such as polycarbonate, ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), or HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene).

Key material features:
- Impact Resistance: Prevents head injuries from falling objects.
- Electrical Insulation: Required for engineers working near live electrical systems.
- Heat Resistance6: Essential for high-temperature environments, such as steel plants.
Material Comparison Table:
| Material | Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | Lightweight, durable, UV-resistant | Engineers in diverse environments |
| ABS | Cost-effective, strong, and rigid | General construction helmets |
| HDPE | High impact resistance, chemical-resistant | Industrial and chemical sites |
These materials ensure safety caps meet rigorous performance standards, offering optimal protection.
How does the work environment influence the choice of safety caps for engineers and architects?
Different work environments present unique hazards, influencing safety cap selection for engineers and architects.
Engineers7 often require helmets with advanced features for hazardous zones, while architects8 prioritize lighter, comfortable designs for inspections.

For Engineers:
- Industrial Sites: Need helmets with electrical insulation and heat resistance.
- Underground Projects: Require caps with integrated lighting systems for visibility.
For Architects:
- Urban Construction: Favor lightweight helmets with a sleek design for prolonged use.
- Renovation Projects: Need helmets that fit well in confined spaces.
Selecting the right helmet ensures maximum safety and adaptability to specific tasks.
What additional features are included in safety caps for engineers working in hazardous environments?
Engineers often encounter extreme conditions requiring specialized helmet features to ensure safety.
Advanced safety caps9 for engineers may include built-in visors, integrated headlamps, and temperature-resistant coatings for enhanced protection.

Key features:
- Chin Straps: Secure the helmet during high-mobility tasks.
- Ventilation Systems10: Prevent overheating in high-temperature zones.
- Communication Tools: Integrated radios for real-time coordination.
- UV Protection: Shields against prolonged sun exposure on outdoor sites.
These features allow engineers to perform efficiently in high-risk settings while ensuring safety.
Why is head protection crucial for architects during on-site inspections?
Architects frequently visit construction sites to ensure design adherence, exposing them to potential hazards.
Head protection is critical for architects to prevent injuries from falling debris, structural failures, or equipment mishaps during inspections.

Common risks for architects:
- Falling Objects: Tools, materials, or debris can cause severe injuries.
- Collapsing Structures: Unstable scaffolding or incomplete frameworks pose threats.
- Slips and Falls: Uneven surfaces increase accident risks.
Equipping architects with proper safety caps mitigates these dangers, ensuring their safety as they focus on quality control and compliance.
Conclusion
Safety caps are essential for engineers and architects, tailored to their unique roles and environments. From material requirements to advanced features, each safety cap is designed to enhance protection, ensure role identification, and adapt to specific site conditions. By understanding these distinctions, construction teams can foster safer, more efficient work environments while meeting industry regulations.
-
Linking this keyword to provide detailed information on how safety caps protect engineers and architects from head injuries on construction sites. ↩
-
Linking this keyword will explain how helmet colors help differentiate roles, improving communication and safety in a busy construction environment. ↩
-
Linking this keyword to provide a deeper understanding of how color coding helps differentiate roles, reducing confusion and enhancing safety protocols. ↩
-
Linking this keyword helps explain the specific use of these colors to signify consulting or design-related roles, clarifying their importance in site inspections and planning. ↩
-
Linking this keyword helps users understand the critical material properties needed to ensure safety and durability in environments with high hazard levels. ↩
-
Linking this keyword highlights the importance of heat-resistant materials in industries like steel production or firefighting, where exposure to extreme temperatures is common. ↩
-
Linking this keyword highlights the specific safety requirements, such as electrical insulation and heat resistance, tailored to engineers’ tasks in high-risk zones. ↩
-
Linking this keyword emphasizes how architects prioritize comfort, weight, and functionality, particularly for site inspections and design reviews. ↩
-
You should link this keyword to explain how advanced helmet designs incorporate protective and functional elements for engineers facing extreme conditions. ↩
-
Linking this keyword highlights the importance of ventilation in preventing heat stress and ensuring comfort during prolonged use in challenging conditions. ↩
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
