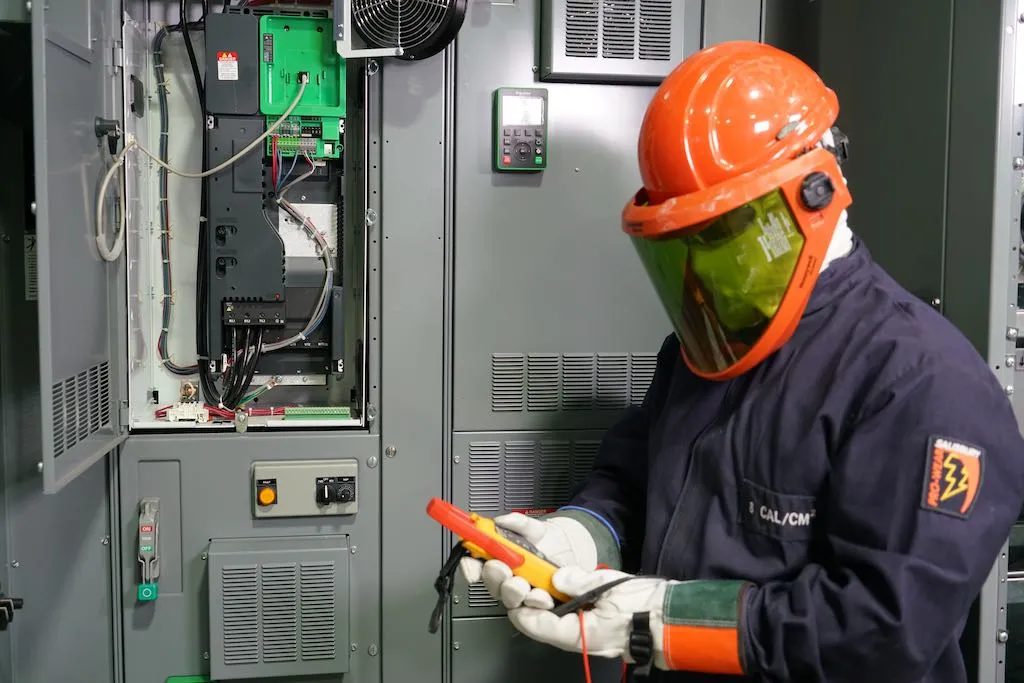

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a critical role in electrical installation work, where workers are exposed to a range of hazards, including electrical shocks, arc flashes, burns, and falls. The use of proper PPE reduces the risk of severe injuries and fatalities, providing an essential layer of defense against unpredictable electrical incidents. Electrical installation work involves close interaction with live circuits, high-voltage equipment, and potentially unstable environments, making PPE indispensable for safety.
Using PPE in electrical installation not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also significantly reduces the likelihood of life-threatening injuries.
What Specific PPE Items are Essential for Electrical Installation Work?
In electrical installation work, PPE must be specifically chosen to guard against electrical hazards, including electrical shock, burns, and arc flashes. Essential PPE items include:
| PPE Item | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Insulated Gloves | Protects hands from electric shock | Made of rubber with insulating properties |
| Arc-Rated Clothing | Shields against arc flash burns | Flame-resistant shirts, pants, and coveralls |
| Safety Goggles | Protects eyes from sparks and debris | ANSI-rated, with side shields or full face coverage |
| Face Shield | Protects face from arc flashes and burns | Arc-rated with clear visibility |
| Hard Hats | Prevents head injuries from impact and electrical shocks | Often arc-rated or with electrical resistance |
| Insulated Footwear | Reduces risk of grounding and shock | Made from non-conductive materials |
| Hearing Protection | Shields against loud noises during arc flashes | Earplugs or earmuffs |
Key PPE Features:
- Insulated Materials: Essential for gloves and footwear to prevent electrical conductivity.
- Arc-Rated Protection: Clothing, face shields, and helmets should meet arc-rating standards to withstand arc flash temperatures.
- Head-to-Toe Protection: Complete coverage is essential, as electricity can strike any part of the body.
How Does PPE Protect Workers from Various Electrical Hazards, such as Shocks, Burns, or Arc Flashes?
Electrical hazards pose a variety of risks, each requiring specific PPE to mitigate the potential injury:
-
Electrical Shock: Insulated gloves and boots protect workers from electrical currents by creating a non-conductive barrier. In situations with live circuits, these items prevent the body from becoming a pathway for current.
-
Burns from Arc Flashes: Arc-rated clothing, face shields, and helmets are designed to withstand high temperatures from arc flashes, which can reach up to 35,000°F. Flame-resistant materials limit burns by preventing the fabric from igniting or melting.
-
Thermal and Chemical Burns: When equipment malfunctions, it can release hot gases or chemicals. Arc-rated and flame-resistant PPE reduces the risk of chemical burns and thermal injuries.
-
Eye and Ear Protection: Arc flashes produce intense light and sound, which can cause eye damage and hearing loss. Safety goggles and hearing protection are essential to protect sensitive organs.
How PPE Prevents Injuries:
- Barrier Against Conductivity: PPE like insulated gloves and boots create a barrier that prevents electricity from reaching the body.
- Heat and Flame Resistance: Arc-rated materials block flames and absorb heat, reducing the severity of burns.
- Protection from Flying Debris: Goggles and shields protect the face and eyes from metal fragments, sparks, or hot gases.
What are the Regulations and Standards for PPE in Electrical Installation Work?
PPE standards in electrical installation work are defined by organizations such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and NFPA (National Fire Protection Association), which set requirements to ensure worker safety.
| Regulatory Body | Relevant Standard | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| OSHA | 29 CFR 1910.335 | Requires use of PPE for electrical protection |
| NFPA | NFPA 70E: Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace | Defines arc-rated PPE and risk assessment |
| ANSI | ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 (Eye Protection), ANSI Z89.1 (Head Protection) | Ensures eye and head protection standards |
| ASTM | ASTM F1506 for Arc-Rated Clothing | Specifies flame-resistant clothing properties |
Key Regulations:
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.335: Outlines general PPE requirements for protection against electrical hazards, including insulation for gloves, face shields, and arc-rated clothing.
- NFPA 70E: Provides detailed guidelines on electrical safety, including PPE selection based on arc flash hazard levels, risk assessments, and minimum PPE categories for different tasks.
- ANSI and ASTM Standards: Ensure that specific PPE items like goggles, helmets, and clothing are tested for impact, insulation, and arc resistance.
These regulations are essential in ensuring electrical safety and compliance, helping employers reduce liability and protect workers from life-threatening accidents.
How Does PPE Use in Electrical Installation Differ from Other Industries?
PPE in electrical installation work has unique requirements, mainly due to the high risk of shock and arc flash, which differ from hazards in other industries like construction or chemical processing.
Differences in PPE for Electrical Work:
-
Insulation: Electrical PPE, such as gloves, boots, and tools, must be non-conductive to prevent electrical currents from passing through the body.
-
Arc Flash Protection: Electrical work PPE must often be arc-rated to protect against the high temperatures of arc flashes. This differs from standard flame-resistant clothing in industries that deal only with heat or fire hazards.
-
High Durability: Electrical PPE undergoes more frequent testing and maintenance, as equipment that degrades over time could fail to provide adequate protection.
-
Complex PPE Combinations: Electrical workers may need to wear multiple layers of PPE, such as insulated gloves with rubber liners, arc-rated coveralls, and helmets with face shields, due to the multifaceted nature of electrical hazards.
Overall, PPE for electrical installation requires a higher level of material quality, insulation, and thermal resistance, which may not be as stringent in other fields where arc flash risks are low or nonexistent.
What Training or Guidelines Should Workers Follow to Ensure Proper Use and Maintenance of PPE in Electrical Installations?
Proper training is essential for workers handling electrical installations to ensure they use PPE effectively and perform regular maintenance checks.
Key Training Areas for Electrical PPE:
- PPE Selection: Workers should be trained to select appropriate PPE based on the specific electrical hazards and standards required for each task.
- Fit and Inspection: Regular inspections for damage, wear, and correct fit are critical, as damaged or poorly fitting PPE can fail to protect in high-risk situations.
- Proper Storage: Insulated gloves, face shields, and arc-rated clothing should be stored in cool, dry areas to prevent damage from UV exposure or moisture.
- Correct Usage: Training should cover the correct sequence for donning and doffing PPE, especially when working in high-voltage environments where insulation and layer integrity are crucial.
- Maintenance: Electrical PPE must be regularly cleaned and tested for insulation resistance and arc-rating compliance, as recommended by manufacturers and industry standards.
Workers must also understand how to respond in an emergency, including knowing when to replace damaged PPE and recognizing the limitations of their protective gear.
How Does the Quality and Material of PPE Affect Its Performance in High-Voltage or High-Risk Environments?
The quality and material of PPE are critical factors that determine its performance and durability in high-risk environments.
High-quality materials like Nomex, Kevlar, and other flame-resistant or insulated materials offer superior protection in high-voltage electrical settings.
Factors Affecting PPE Performance:
- Material Insulation: High-quality rubber and composite materials in gloves and boots provide better electrical insulation, essential for protection in high-voltage environments.
- Arc-Rated vs. Flame-Resistant: Arc-rated clothing is specifically designed for the intense heat and energy of arc flashes, unlike standard flame-resistant clothing which may not withstand these conditions.
- Durability Under Stress: PPE made from durable materials is more resistant to wear and tear, essential for maintaining safety in high-stress environments where exposure to sharp objects, high temperatures, and chemicals is common.
- Layering and Fit: Well-fitted, multi-layer PPE ensures that all parts of the body are protected without gaps, which is vital in electrical work where high voltages can arc.
High-quality PPE that is made from the right materials can be the deciding factor between minor burns and serious injury, particularly in high-risk electrical work. Proper investment in quality PPE helps organizations prevent accidents and maintain safer work environments.
Conclusion
In electrical installation work, PPE is not just a safety precaution—it’s a critical line of defense against potentially deadly hazards like arc flashes, electrical shocks, and thermal burns. From insulated gloves and arc-rated clothing to face shields and hard hats, each piece of PPE is designed to mitigate specific risks. Adherence to industry standards, proper training, and consistent maintenance are essential for ensuring PPE performs effectively in these high-risk environments.
By understanding the specific PPE requirements for electrical work and emphasizing proper usage and maintenance, both workers and employers can create a safer, compliant workplace, reducing the likelihood of severe injuries or fatalities.
Zion Zhang
Recent Posts
 Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […]
Color Consistency: The Delta-E Standard and the End of the “Clown Suit” Effect2026年2月4日In the corporate world, a uniform is a brand’s […] Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […]
Why Zippers Fail (and How We Prevent It): The Engineering of Closure Reliability2026年2月4日In the hierarchy of industrial garment components, the […] The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […]
The Anatomy of a Seam: Engineering Durability at the Needle Point2026年2月4日In the world of industrial workwear, the fabric gets all […] Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […]
Future Lab PPE Trends: The Convergence of Lightweight Protection & Sustainability2026年1月28日In the sterile corridors of pharmaceutical R&D, biotech […] Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […]
Chemical Protection Classes A/B/C: The Definitive Guide to Risk-Based PPE Selection2026年1月28日In the hazardous materials (HazMat) industry, […] Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
Freezer Gloves & Boots Trends: The Intersection of Thermal Physics and Grip Technology2026年1月28日In the unforgiving environment of a -30°C cold storage […]
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
- +86-17330061805
