Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Are You Looking For Personal Protective Equipment(PPE)?
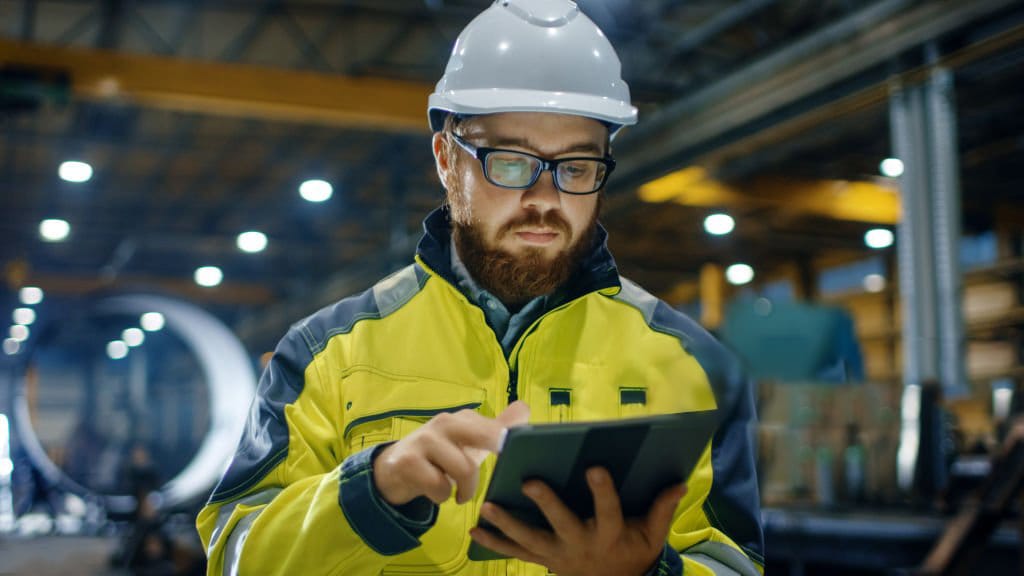
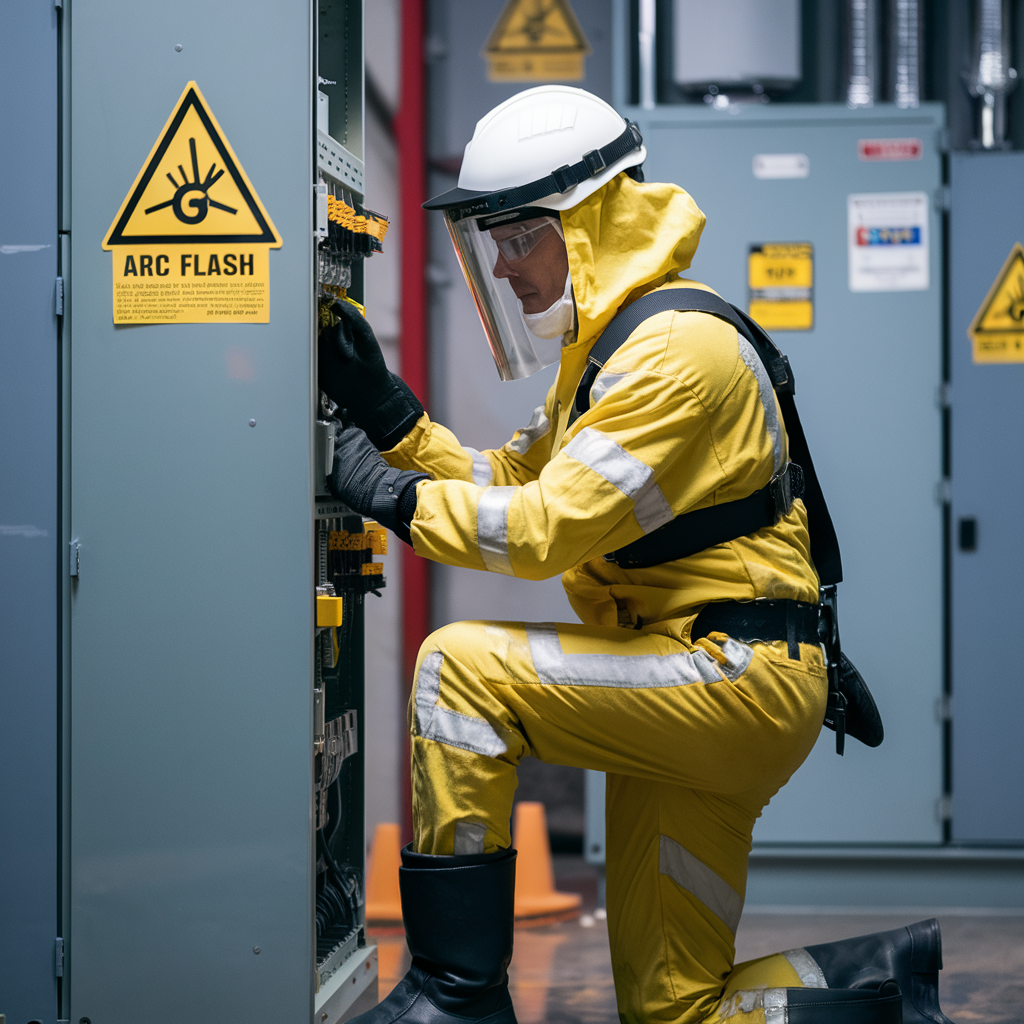
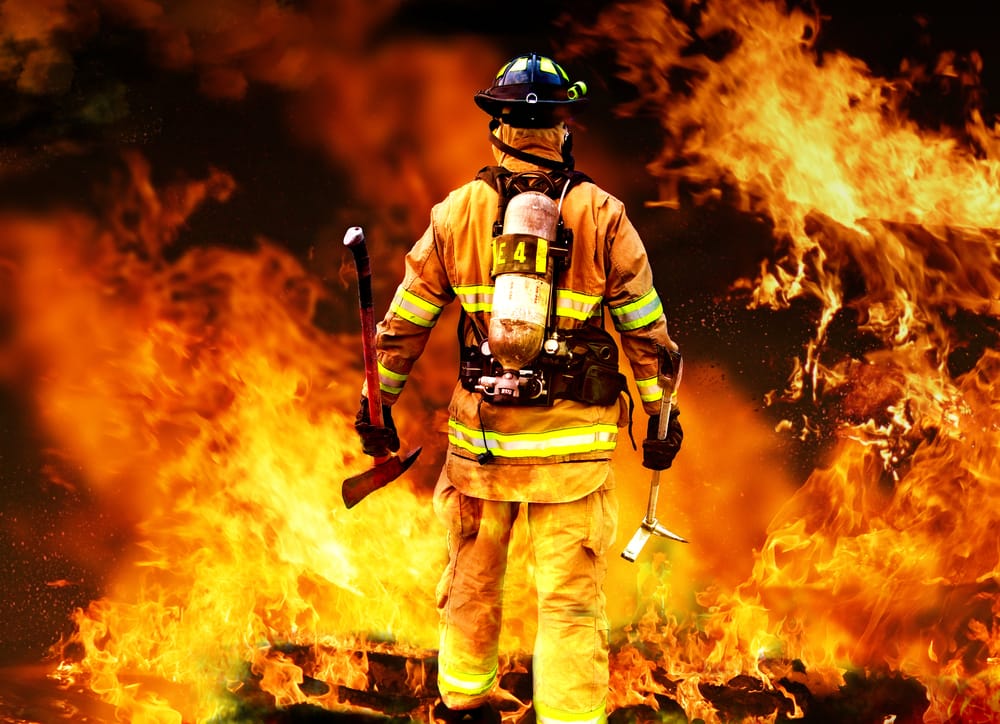
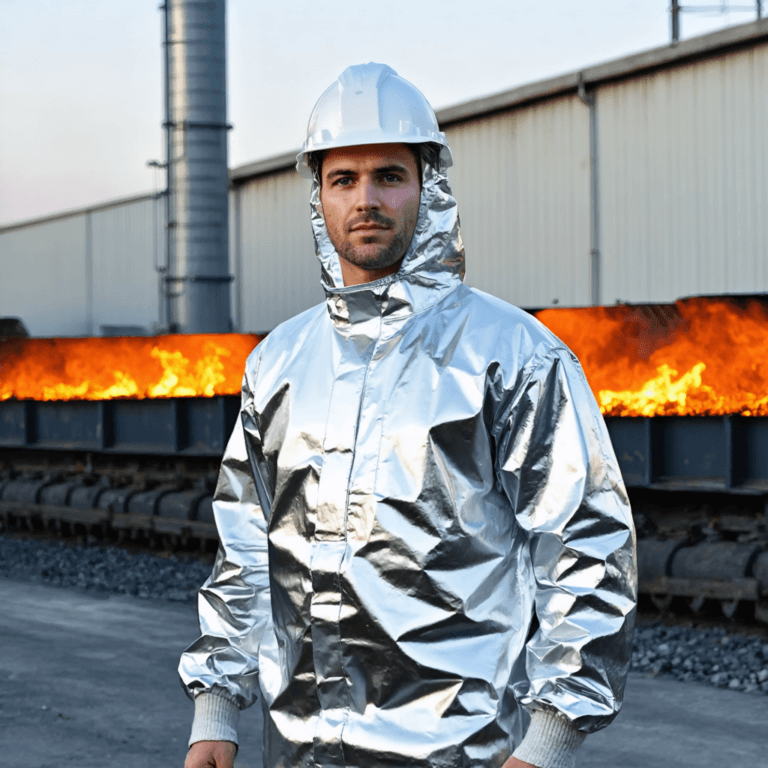
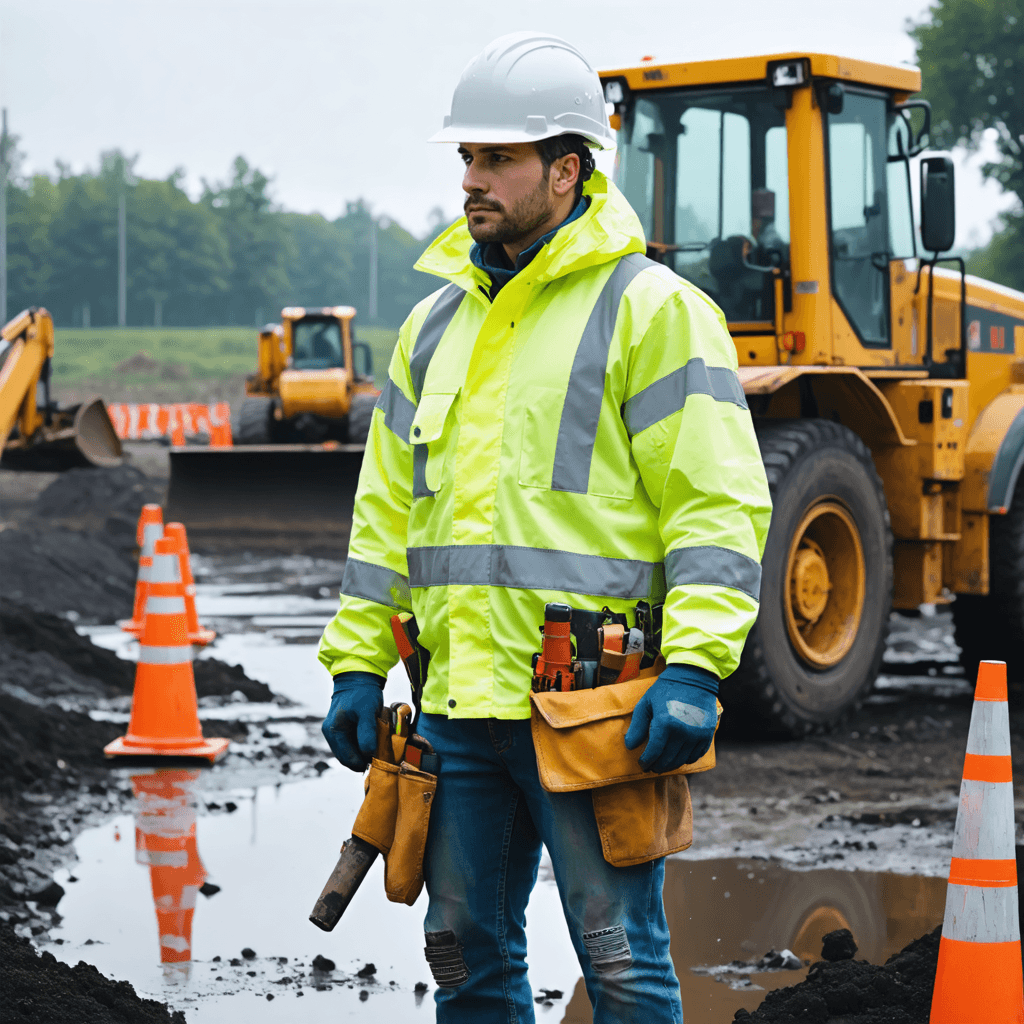
WorkwearSolutions is a leading manufacturer of comprehensive Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), offering an extensive product range that includes Arc Flash Protective Clothing, Flame-Resistant Apparel, Metaltech Gear, High-Visibility Workwear, Outdoor Jackets, Conductive Suits, Military Uniforms, Aluminized Clothing, Chemical Protection Garments, Cooling Vests, and Uniforms. Our PPE production facility in China strictly adheres to ANSI, API, DIN, GOST, BS, JIS, and GB standards, as well as specific client requirements.
We provide expert, all-in-one solutions designed to protect personnel working in high-risk environments involving hazards such as arc flashes, electric fields, extreme heat, flash fires, explosions, chemicals, and biological threats. Our services support both domestic and international clients across sectors, including power generation, emergency fire protection, petroleum and petrochemicals, and a wide range of industrial and mining operations.
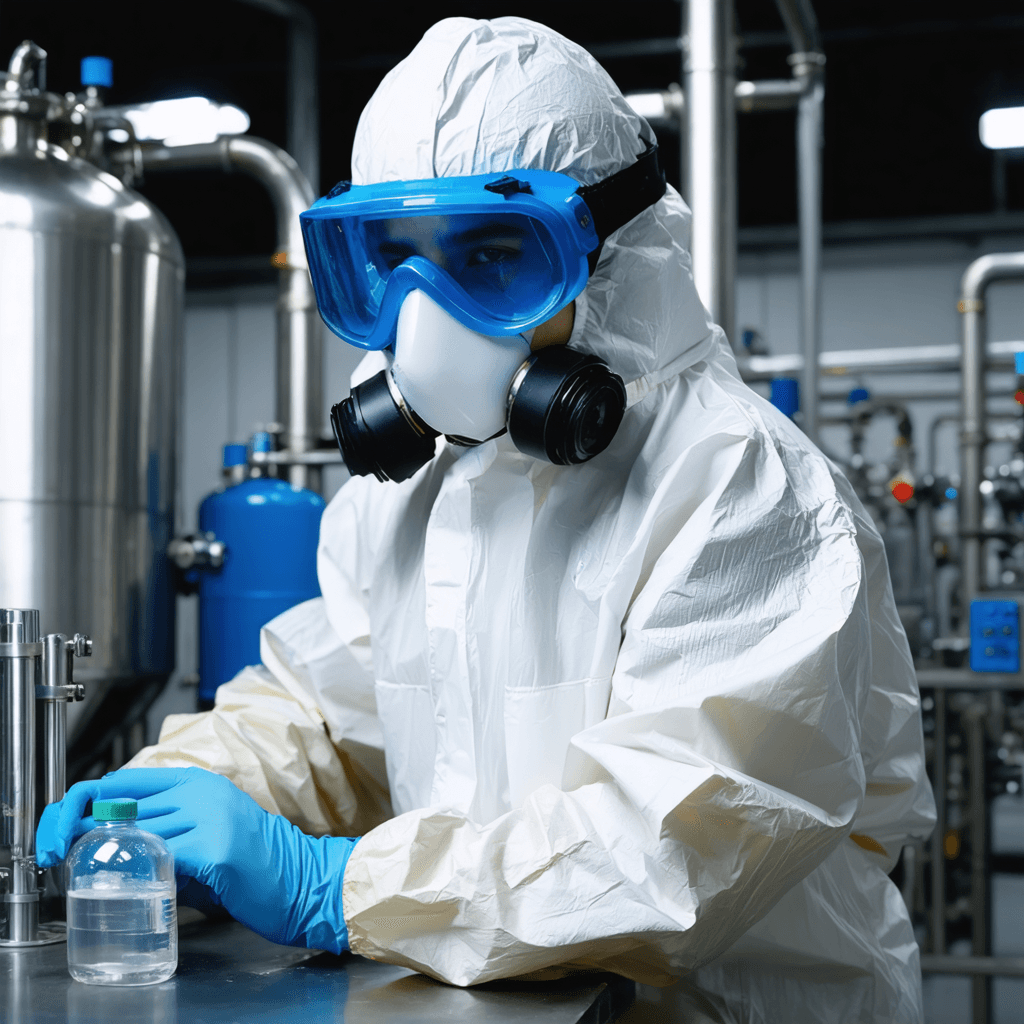
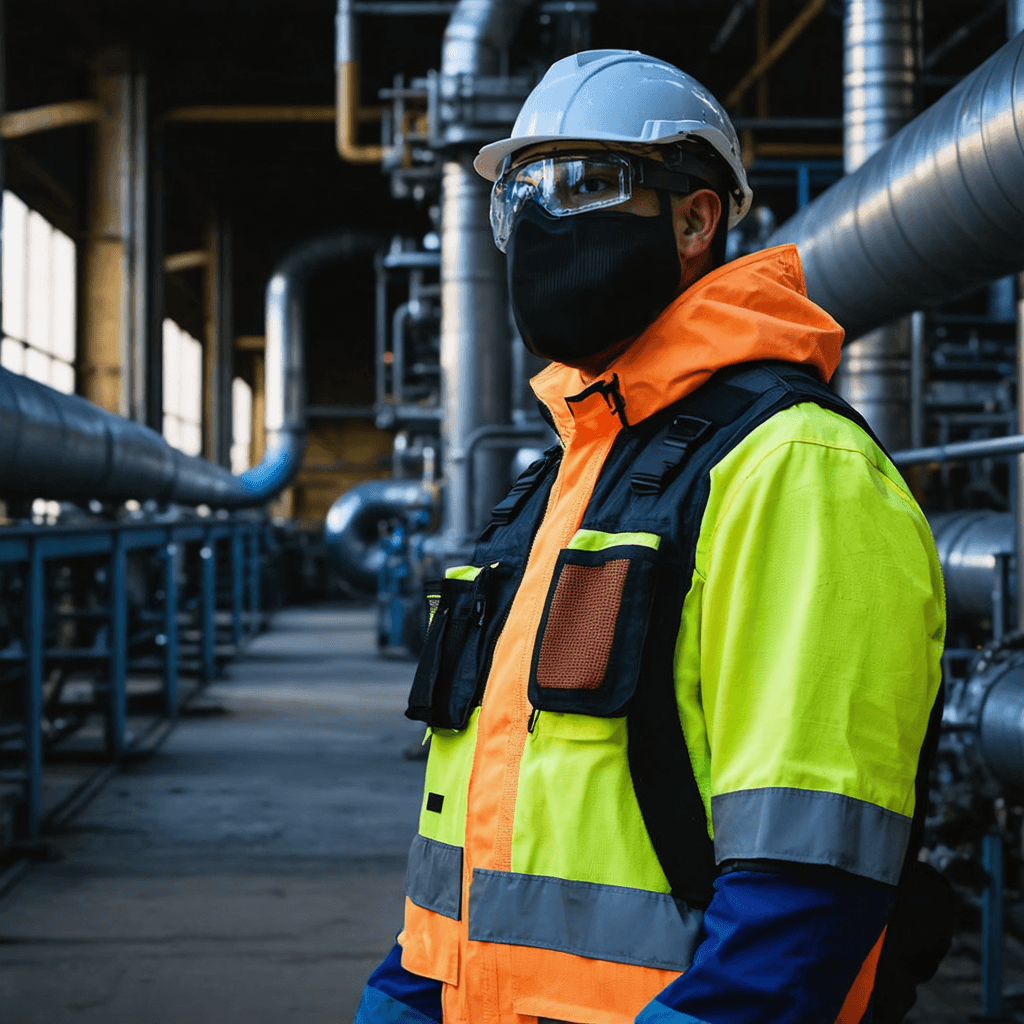
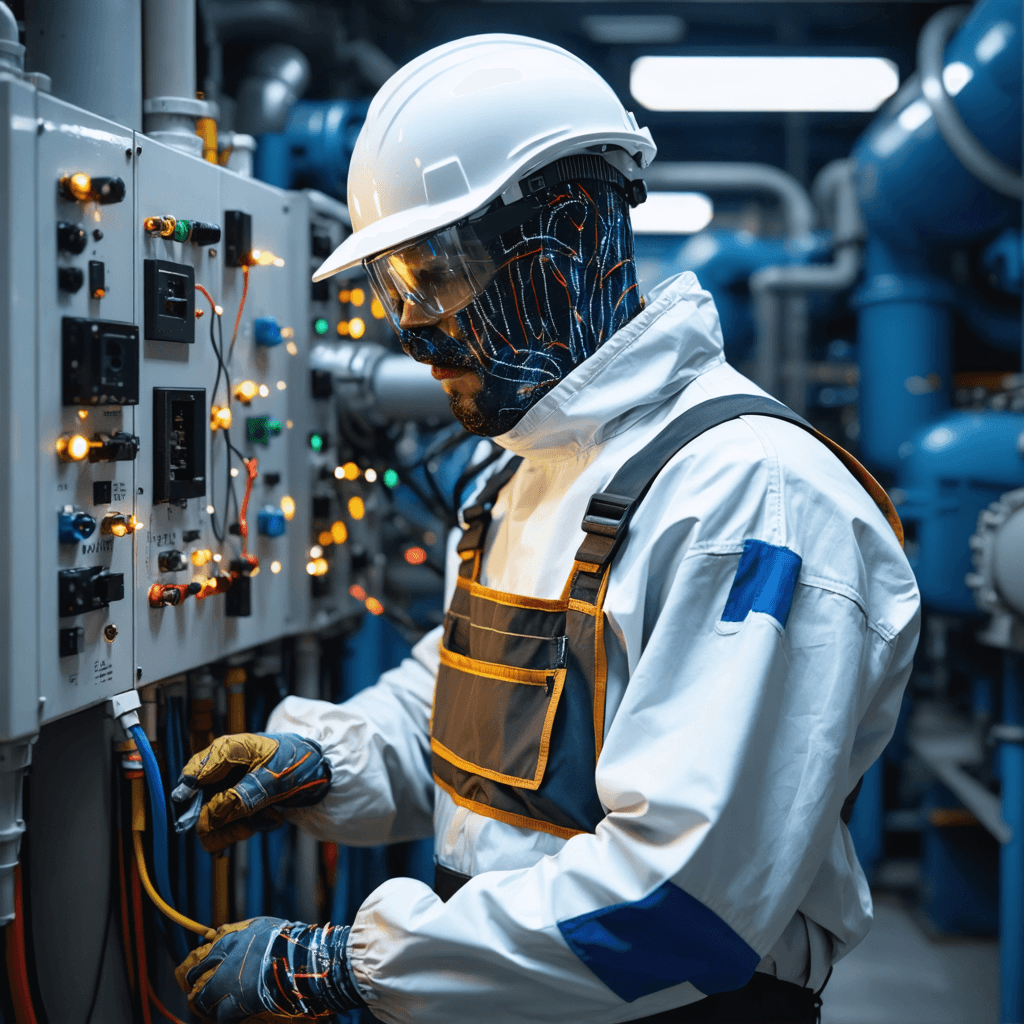









REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
The Ultimate Guide of Personal Protective Equipment(PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Types, Uses and More
Chapter 1
What Are Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)?
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to specialized clothing, gear, and accessories worn to minimize exposure to workplace hazards that can cause serious injuries or illnesses. These hazards may be physical, chemical, biological, or environmental, and PPE serves as a critical barrier between workers and potential risks, enhancing their safety on the job.
PPE is crucial in industries where employees are exposed to potentially dangerous environments, such as construction, healthcare, chemical processing, and emergency services. It helps prevent injuries like burns, respiratory complications, and impact injuries by acting as a first line of defense, supplementing engineering controls and safe work practices.
Choosing appropriate PPE requires a thorough assessment of workplace hazards and ensures that gear meets regulatory standards like ANSI, OSHA, and other international guidelines. Proper fit, durability, and training on correct use are essential to maximize its effectiveness.
In short, PPE is a foundational element of workplace safety, protecting workers from immediate hazards and promoting a culture of safety across diverse industries.
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
Get in Touch
- +86-17330061805
Address
- No.7 Building, No.63, Jianda Road, Huojiatun Village, Loudi Town, Luancheng District, Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province, China
Chapter 2
Types of Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) and Their Functions

Arc Flash Protective Clothing

Flame Resistant Clothing

Military Clothing
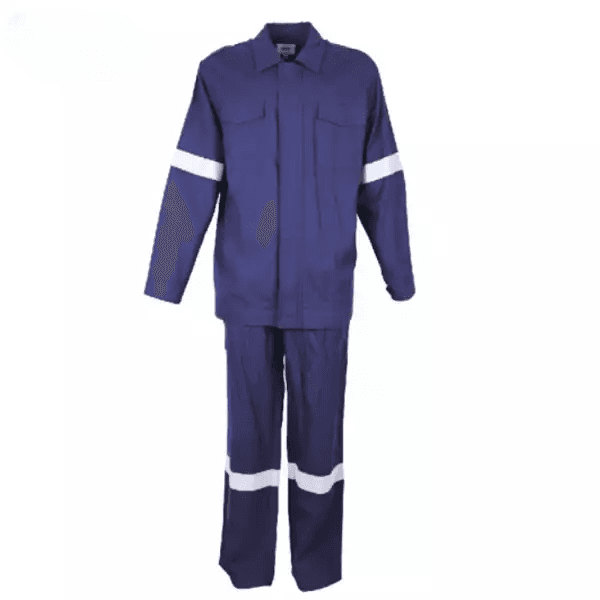

Metaltech Clothing
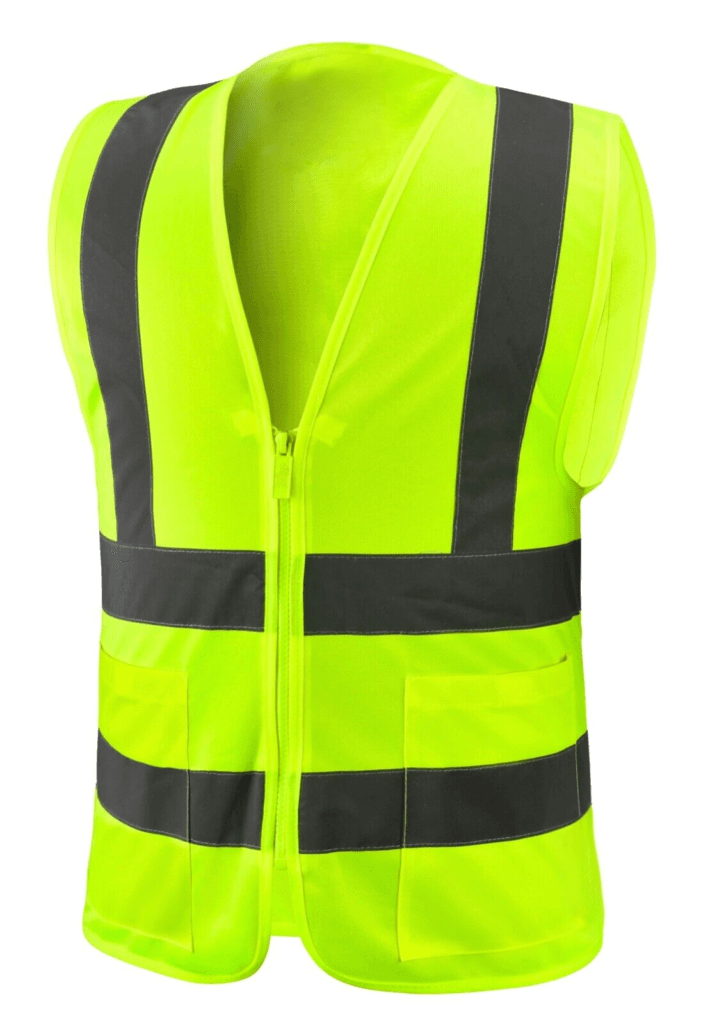

High-Visibility Clothing
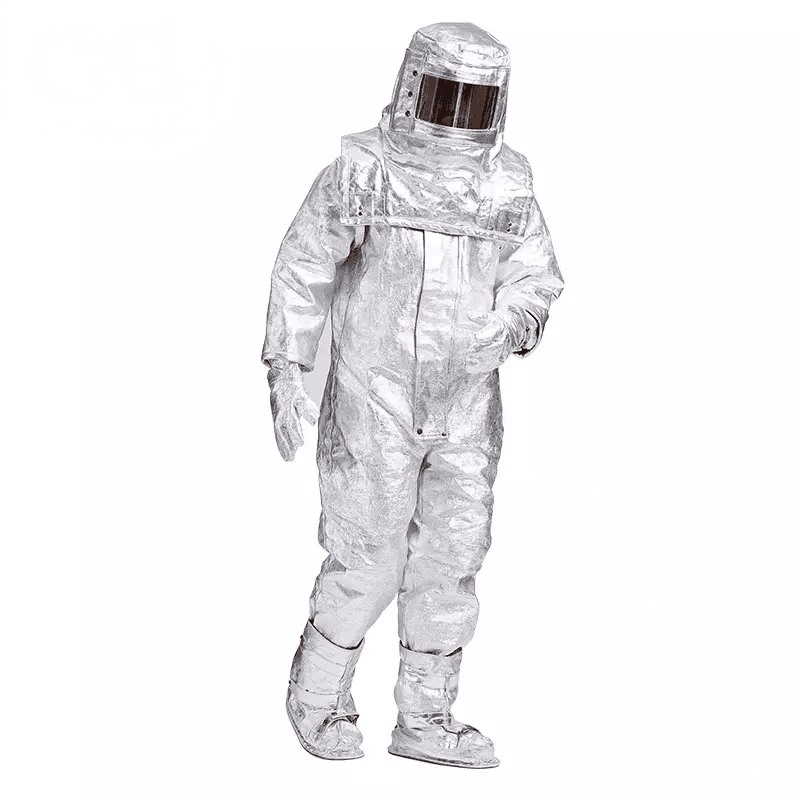

Aluminized Clothing
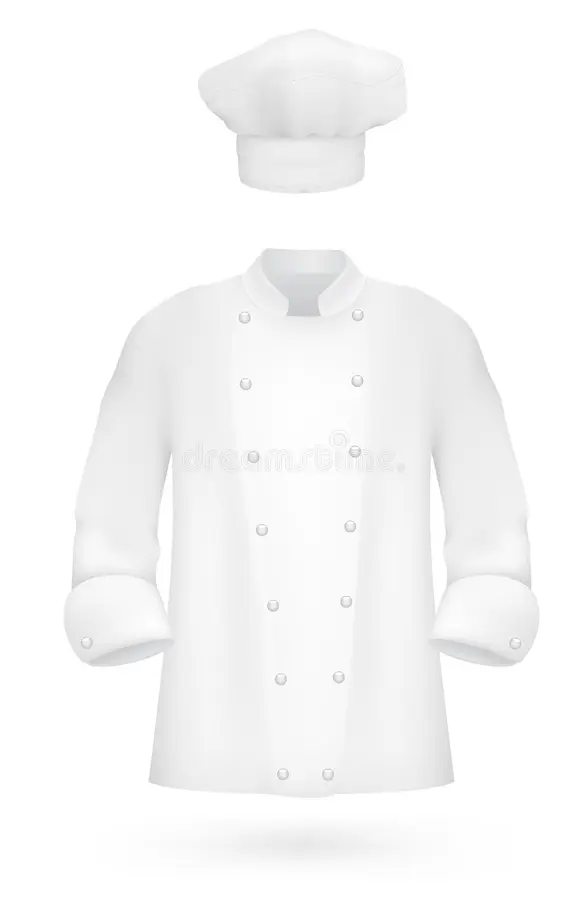

Uniform

Contact us to
Customize your PPE
The primary function of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is to reduce the risk of injury, illness, or harm in hazardous work environments. PPE acts as a barrier between workers and potential hazards, addressing various safety needs based on the type of work performed. Here’s a breakdown of the core functions of PPE:
- Protection Against Physical Hazards
- Impact and Falling Objects: Helmets and hard hats protect the head from blows or falling objects.
- Cuts and Abrasions: Gloves and protective suits safeguard hands and body against sharp edges, rough surfaces, and other cut hazards.
- Compression and Crushing: Steel-toed boots and reinforced gloves prevent injuries from heavy objects or machinery.
- Protection from Chemical and Biological Hazards
- Chemical Exposure: Chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and suits prevent harmful chemicals from contacting the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Biohazard Protection: Masks, gloves, gowns, and face shields minimize exposure to bacteria, viruses, and other biological risks in healthcare and lab settings.
- Shielding Against Environmental Hazards
- Extreme Temperatures: Heat-resistant clothing and aluminized suits protect against high-temperature work environments, such as foundries and firefighting.
- Weather Protection: High-visibility jackets and waterproof clothing ensure safety in outdoor and low-visibility conditions, protecting against rain, cold, and wind.
- Respiratory Protection in Hazardous Air Conditions
- Dust and Particles: Respirators and masks filter harmful particles in construction, mining, and industrial settings.
- Toxic Gases and Fumes: Specialized respirators and gas masks shield workers from toxic inhalants present in chemical processing or waste management.
- Hearing and Vision Safety
- Noise Reduction: Earplugs and earmuffs protect against hearing loss in high-decibel environments, like construction and manufacturing.
- Eye Safety: Safety goggles and face shields prevent eye injury from flying debris, splashes, and glare in welding, woodworking, and laboratory work.
- Enhanced Visibility and Identification
- High-Visibility Gear: Reflective vests and bright-colored clothing ensure workers are visible in low-light or hazardous conditions, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Identification and Role Distinction: Uniforms and marked PPE can help identify roles, responsibilities, and authorized personnel on a worksite, improving operational safety.
In sum, PPE functions as a comprehensive safety solution tailored to mitigate specific risks, ensuring workers are protected and compliant with safety standards in various high-risk environments.
Chapter 3
What Are Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) Used For?
Construction and Mining
In construction and mining, workers are exposed to a wide range of physical hazards, from falling objects to heavy machinery and dangerous work environments. As a result, helmets are critical for protecting against head injuries caused by falling debris or accidental impacts. Gloves are used to safeguard hands from sharp materials, equipment-related injuries, and harsh conditions. Protective footwear, such as steel-toe boots, prevents foot injuries from heavy or sharp objects and provides traction on unstable surfaces. High-visibility clothing is essential to ensure workers are easily seen, reducing the risk of accidents involving heavy equipment or vehicles. Overall, this combination of PPE plays a pivotal role in preventing severe injuries and maintaining a safe working environment.
Healthcare
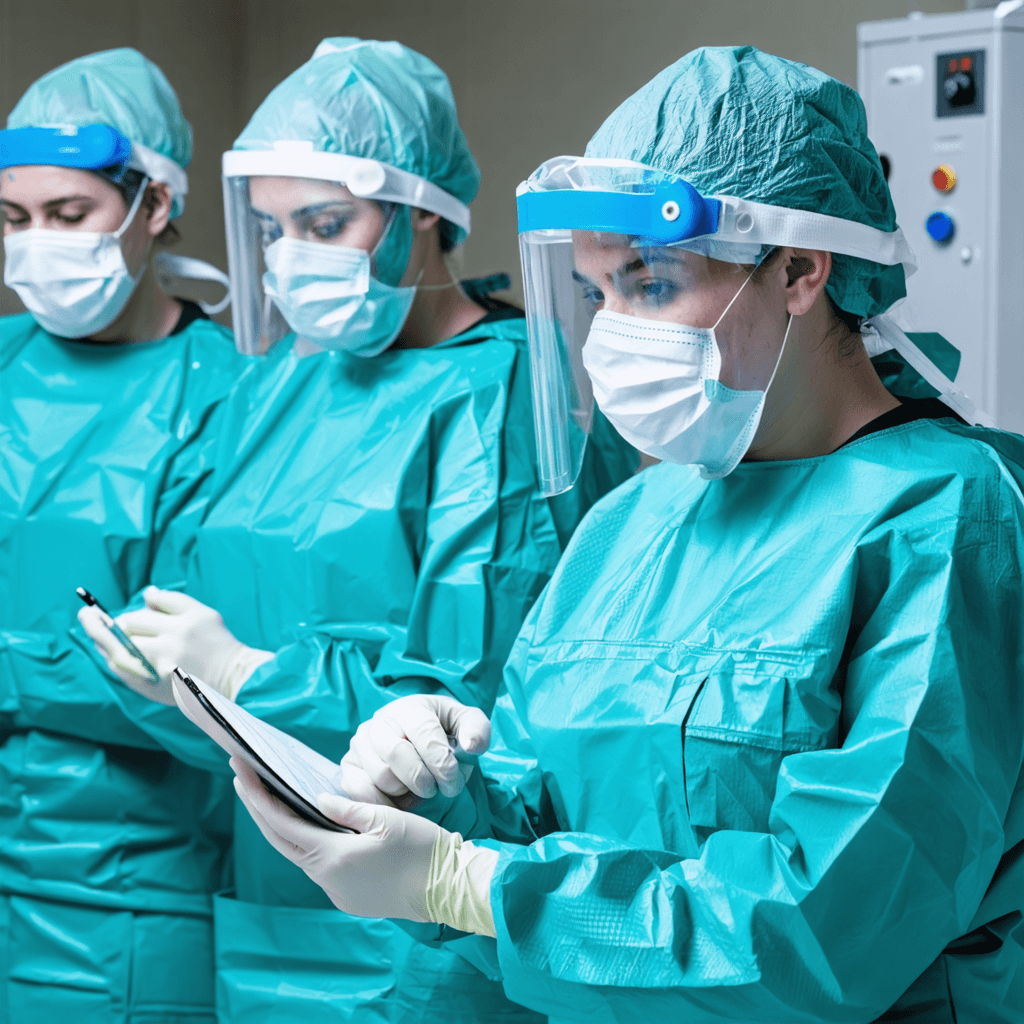
Healthcare professionals are frequently in close contact with patients and exposed to various biological hazards, including infectious diseases, viruses, and bacteria. PPE in this field is designed to prevent the transmission of pathogens and ensure the safety of medical personnel and patients alike. Gloves offer a barrier to protect hands from contamination, while face shields and masks protect the mouth, nose, and eyes from infectious droplets. Gowns and isolation suits prevent healthcare workers’ clothing and skin from coming into contact with biological fluids. In high-risk situations, advanced respirators like N95 masks are used to filter airborne particles and protect against respiratory infections. This PPE setup is crucial for infection control in hospitals, clinics, and emergency settings.
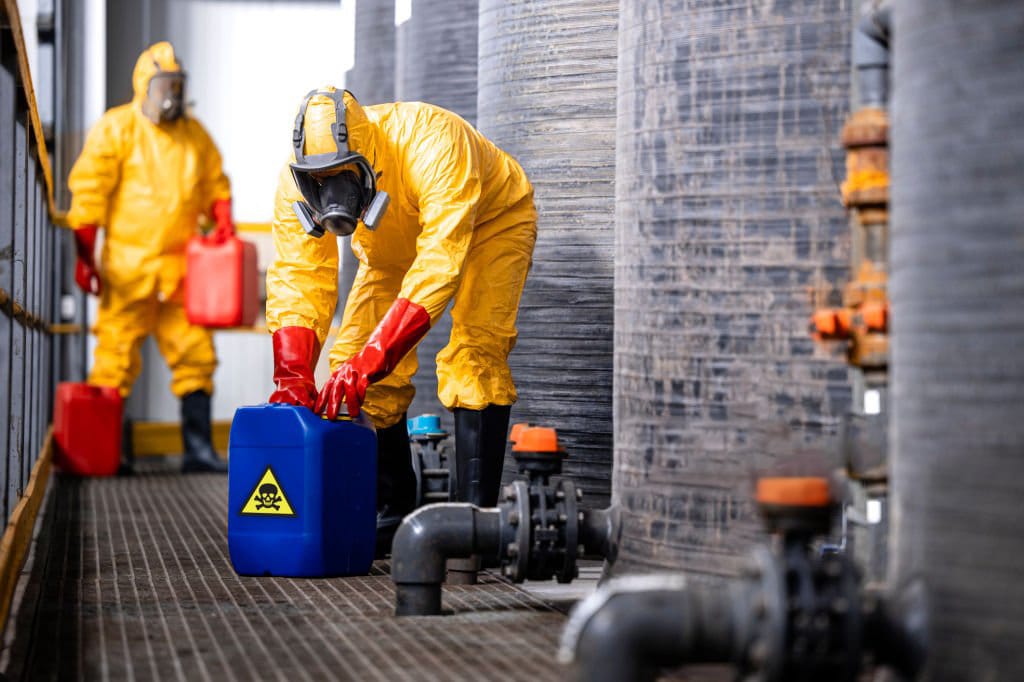
Chemical Processing
Chemical processing environments often involve handling hazardous and toxic substances, making comprehensive protection essential. Workers require full-body chemical suits that resist penetration by chemicals and prevent skin exposure. Respirators are used to filter dangerous vapors, fumes, and particulate matter, ensuring safe breathing in environments where air contamination is a risk. Chemical-resistant gloves protect hands from corrosive substances, while face shields and safety goggles provide a protective barrier for the eyes and face. This type of PPE is critical to prevent chemical burns, respiratory issues, and exposure-related health complications, ensuring worker safety in industrial and laboratory settings.
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector poses numerous hazards, including the risk of explosions, fire, toxic gas leaks, and exposure to volatile chemicals. Flame-resistant clothing is crucial to protect workers from flash fires and thermal burns, while anti-static garments help prevent sparks that could ignite flammable gases. Helmets provide protection from falling debris and impact injuries, and gloves shield hands from sharp tools and materials while offering heat resistance. Specialized boots are designed to prevent punctures and resist chemical exposure while providing traction on slippery surfaces. This carefully selected PPE is vital for maintaining safety in oil refineries, offshore rigs, and gas extraction sites, where even minor accidents can have catastrophic consequences.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing settings, workers are often exposed to a variety of mechanical hazards, such as flying debris, loud noise levels, and heavy machinery. Safety glasses and goggles are used to protect the eyes from metal shavings, dust, and sparks. Ear protection, including earplugs or earmuffs, is essential in noisy environments to prevent hearing damage over time. Machine guards and protective barriers are also considered critical components of PPE to shield workers from accidental contact with moving parts. By using the appropriate PPE, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of common workplace injuries such as eye damage, hearing loss, and machine-related accidents.
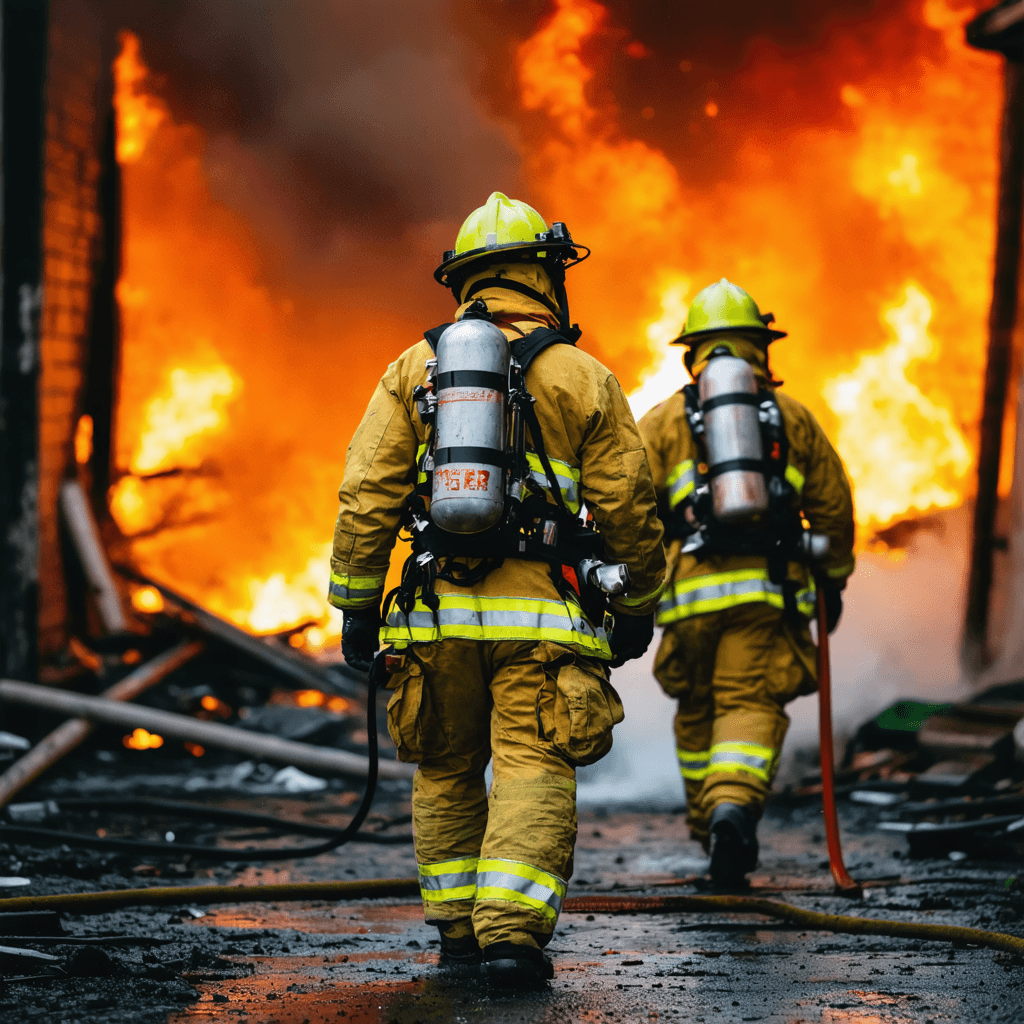
Emergency Services
Emergency responders, including firefighters and first responders, often work in life-threatening situations and need robust PPE to handle extreme conditions. Flame-retardant suits provide protection from high heat and flames, while heat-resistant helmets with face shields protect the head and face from falling debris and intense temperatures. Firefighters also rely on self-contained breathing apparatuses (SCBA) to ensure a clean air supply when entering smoke-filled or toxic environments. Durable gloves offer dexterity while shielding hands from burns, cuts, and chemical exposure. This level of PPE is designed to keep emergency service personnel safe while they carry out rescue and firefighting missions, where every second counts and the risk of injury is high.
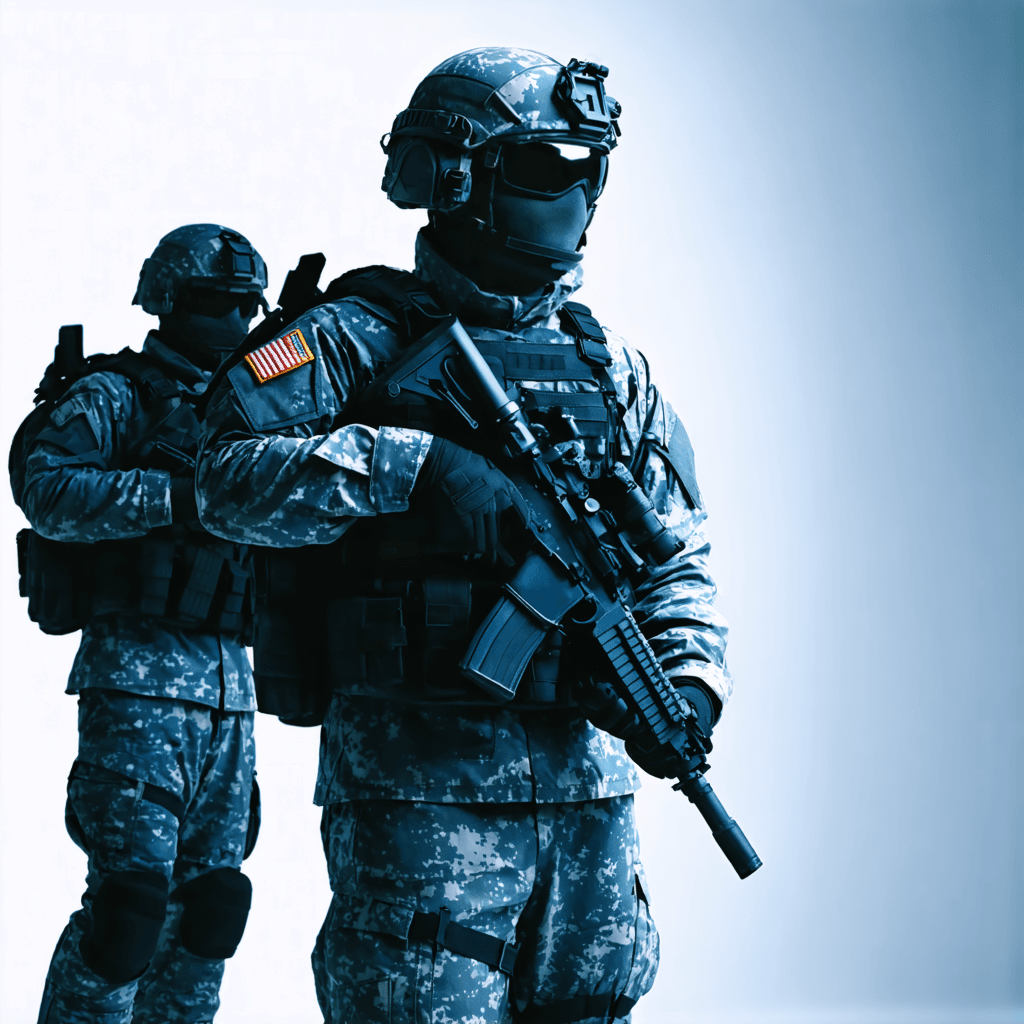
Military
Military clothing is a specialized category of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) designed to protect armed forces personnel from a variety of environmental, physical, and combat-related hazards. Due to the unique and high-risk nature of military operations, this type of PPE must provide both comprehensive protection and adaptability to different combat scenarios, climates, and operational demands.
By understanding and implementing these industry-specific PPE requirements, organizations can create safer working environments and significantly reduce the risk of injuries and health-related incidents.
Chapter 4
What Are Key Components of Personal Protective Equipment(PPE)
Head Protection
Head protection is essential for shielding workers from head injuries caused by impact, falling objects, or electrical hazards. Helmets, hard hats, and bump caps are the primary forms of head protection.
- Helmets and Hard Hats: Constructed from durable, impact-resistant materials, they are used in environments like construction sites, mining, and heavy industry, where falling debris or accidental head impacts are common. Certain helmets are designed with additional features, such as built-in visors or earmuffs, to offer combined protection.
- Bump Caps: Lightweight and designed for environments where the risk of head injury is low, bump caps protect against minor bumps and scrapes, commonly used in manufacturing and warehouse settings.
Eye and Face Protection
Protecting the eyes and face from potential hazards is critical in many industries. Safety goggles, face shields, and visors provide comprehensive protection from harmful threats such as chemical splashes, flying debris, or intense light and radiation.
- Safety Goggles: These create a secure seal around the eyes, preventing chemicals, dust, and particles from making contact. They are essential in laboratories, construction work, and chemical processing facilities.
- Face Shields: Offering full-face coverage, face shields protect against splashes, sparks, and flying debris, commonly used in metalworking, welding, and medical procedures where fluid exposure is a concern.
- Visors: Made from impact-resistant materials, visors are often attached to helmets to provide a transparent shield that guards against projectiles and harsh environmental conditions, such as in forestry and industrial operations.
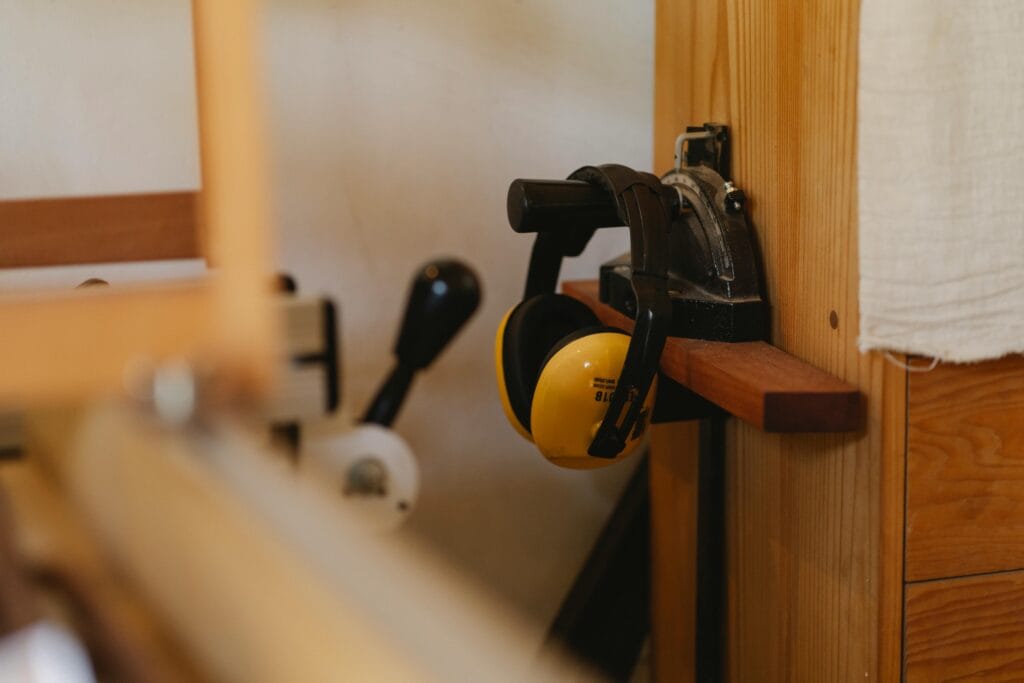
Hearing Protection
High-decibel environments, such as construction sites, manufacturing plants, and airports, pose a significant risk of hearing loss. Earplugs and earmuffs are used to minimize this risk by reducing noise exposure.
- Earplugs: Made from soft, flexible materials, earplugs fit snugly inside the ear canal to block harmful sound waves. They are ideal for continuous use and can be disposable or reusable.
- Earmuffs: Earmuffs cover the entire ear, creating a sound barrier. They are designed with cushioned ear cups and an adjustable headband for comfort and are particularly effective in extremely loud environments, such as heavy machinery operation areas.
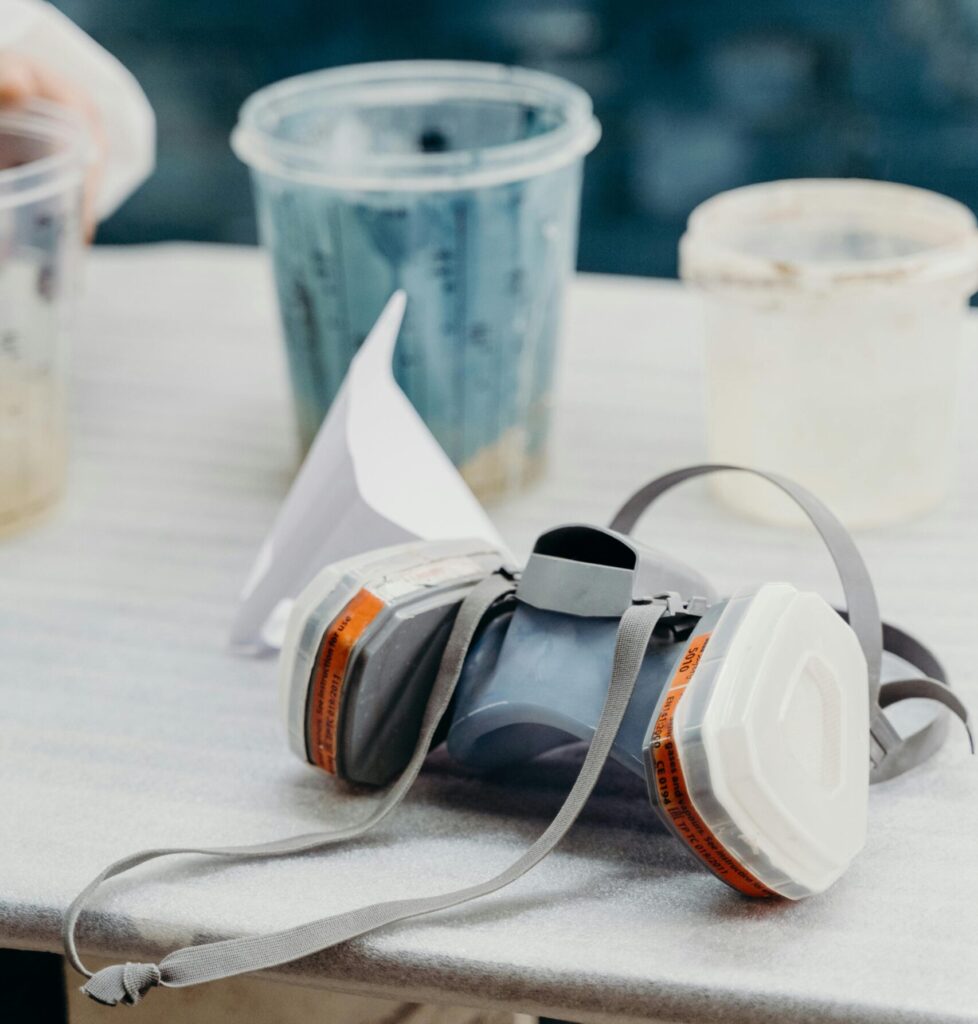
Respiratory Protection
Protecting the respiratory system is crucial in environments where airborne hazards like dust, fumes, smoke, or toxic gases are present. Respiratory protection devices include masks and respirators that filter harmful particles or provide a clean air supply.
- Masks: Simple surgical masks or cloth masks provide basic protection against airborne particles and are widely used in healthcare and settings where exposure to infectious agents is a risk.
- Respirators: More advanced than masks, respirators come in various forms, such as N95 respirators that filter fine particles or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) that use a fan to blow filtered air to the user. Full-face respirators are used in highly contaminated environments, such as chemical plants, to ensure comprehensive protection for the face and respiratory tract.
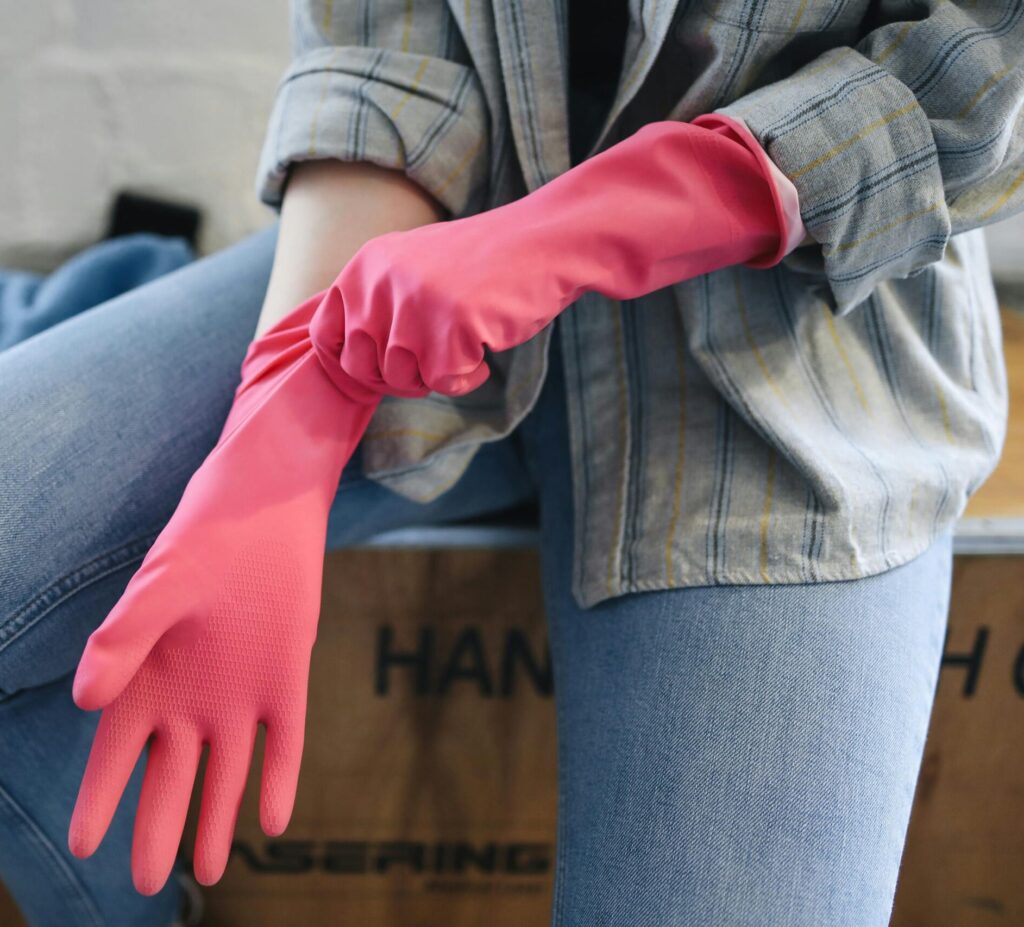
Hand Protection
Hands are highly susceptible to a variety of workplace injuries, including cuts, burns, punctures, and chemical exposure. Gloves made from specific materials cater to different risks and applications.
- Nitrile Gloves: Resistant to punctures and a wide range of chemicals, nitrile gloves are commonly used in laboratories, healthcare, and chemical handling.
- Rubber Gloves: Suitable for handling caustic substances and providing a waterproof barrier, rubber gloves are frequently used in cleaning and chemical industries.
- Leather Gloves: Ideal for protection against abrasions and sparks, leather gloves are durable and used in construction, welding, and heavy-duty tasks.
- Kevlar Gloves: Made from a cut-resistant and heat-resistant material, Kevlar gloves offer superior protection in environments involving sharp tools and high temperatures, such as in glass handling or metal fabrication.
Body Protection
Specialized protective clothing shields the body from various environmental hazards, from extreme heat to chemical splashes and poor visibility.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Designed for use in high-heat or fire-prone environments, such as in firefighting or oil and gas operations, flame-resistant clothing minimizes the risk of burns.
- High-Visibility Clothing: Often required for roadwork, construction, and emergency response, high-visibility vests and jackets feature reflective materials to ensure workers are easily seen, even in low-light conditions.
- Chemical-Protective Suits: These suits are made from materials that resist permeation by hazardous substances, providing full-body coverage to prevent skin contact in chemical processing or hazardous waste cleanup.
Foot Protection
The feet are vulnerable to injuries from heavy objects, punctures, and exposure to chemicals. Protective footwear, such as steel-toe boots and chemical-resistant shoes, is essential for maintaining foot safety in industrial and construction settings.
- Steel-Toe Boots: Reinforced with a steel or composite cap, these boots provide protection against impact and compression injuries, making them a staple in construction, manufacturing, and mining.
- Chemical-Resistant Footwear: Made from materials like rubber or PVC, this footwear is designed to prevent chemical burns and provide a waterproof barrier in environments where workers are exposed to harmful substances. Additionally, features like slip-resistant soles help prevent falls on wet or oily surfaces.
By incorporating the appropriate PPE tailored to their specific threats, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and create safer working environments for their employees. Each component of PPE plays a vital role in comprehensive workplace safety, ensuring that workers remain protected from a multitude of occupational hazards.
Chapter 5
How to Conduct a Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) Risk Assessment
Conducting a thorough PPE risk assessment is a crucial step in ensuring workplace safety and protecting employees from potential hazards. A well-executed assessment helps to identify and analyze risks, determine the need for specific PPE, and ensure that protective measures are adequate. Here’s a detailed guide on how to carry out an effective PPE risk assessment:
Identify Workplace Hazards
The first step in a PPE risk assessment is to identify all potential hazards present in the work environment. This involves conducting a comprehensive evaluation of the worksite, including physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic risks. For example:
- Physical Hazards: Falling objects, sharp tools, noise levels, extreme temperatures, or slippery surfaces.
- Chemical Hazards: Exposure to harmful substances such as acids, solvents, or toxic fumes.
- Biological Hazards: Pathogens, viruses, or bacteria, particularly relevant in healthcare settings.
- Ergonomic Hazards: Risks associated with repetitive motions, awkward postures, or heavy lifting. Using methods like visual inspections, reviewing accident and incident reports, and consulting with employees about their daily safety concerns can provide valuable insights into the specific dangers that need addressing.
Analyze the Nature of the Hazards
Once the hazards have been identified, the next step is to analyze each hazard to understand the nature and extent of the risk it poses. This involves considering:
- Frequency and Duration of Exposure: How often and for how long are workers exposed to the hazard?
- Severity of Potential Injury or Illness: What is the worst-case scenario if the hazard leads to an incident? For example, a chemical spill may cause severe burns or respiratory problems.
- Affected Employees: Which workers are at risk, and do certain groups (e.g., those with underlying health conditions) require additional protection?
Evaluate Existing Safety Measures
Before recommending PPE, evaluate the effectiveness of current safety measures in place. Assess whether engineering controls (like machine guards or ventilation systems) and administrative controls (such as safe work practices or training programs) adequately minimize the risks. PPE should be considered the last line of defense when other controls are insufficient. This step ensures that PPE is used appropriately and not as a substitute for more effective hazard mitigation strategies.
Determine PPE Requirements
Based on the analysis, determine what types of PPE are needed to provide adequate protection against the identified risks. This decision should be tailored to each hazard type:
- Head Protection: For workers at risk of head injuries from falling objects or accidental impacts.
- Eye and Face Protection: For tasks involving flying debris, chemical splashes, or harmful light radiation.
- Respiratory Protection: When there is a risk of inhaling dangerous gases, dust, or biological agents.
- Hand and Skin Protection: To guard against cuts, chemical burns, or heat exposure.
- Hearing Protection: For environments with consistent exposure to high noise levels, like construction sites. Specify the appropriate PPE for each job task and ensure that it meets industry standards and regulations, such as those from OSHA or ANSI.
Conduct a Fit and Suitability Assessment
PPE must be well-suited to the worker and the specific tasks they perform. Conduct a fit assessment to ensure that PPE, such as respirators or safety goggles, provides a secure and comfortable fit for every employee. Poorly fitted PPE can lead to reduced effectiveness and discomfort, making workers less likely to use it properly. Consider the working conditions as well, such as whether the PPE can withstand extreme heat, cold, or exposure to moisture.
Document and Communicate Findings
Clearly document the results of the PPE risk assessment, detailing identified hazards, the selected PPE, and the rationale behind each choice. This documentation should be shared with management and the workforce to promote transparency and understanding of safety protocols. Include guidelines on proper PPE use, maintenance, and storage. Regularly update this documentation to reflect any changes in the work environment or updates to safety regulations.
Implement Training and Education
Once PPE has been selected, provide comprehensive training to employees on its proper use, care, and limitations. Workers should understand how to correctly wear PPE, how to inspect it for damage, and the procedures for replacing worn or defective items. Emphasize the importance of using PPE consistently and correctly to maximize safety. Periodic refresher courses can help reinforce good practices and ensure compliance.
Review and Update the Risk Assessment Regularly
A PPE risk assessment is not a one-time exercise. It should be reviewed and updated regularly or whenever there are changes in the workplace, such as new machinery, processes, or materials. Additionally, analyze incident reports and near-misses to identify areas where PPE or other safety measures may need improvement. Continuous evaluation ensures that the risk assessment remains relevant and effective in protecting workers.
By following these steps, organizations can conduct a comprehensive PPE risk assessment that ensures appropriate protection for their employees while fostering a proactive approach to workplace safety.
Chapter 6
Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) are critical to ensuring that it remains effective in providing protection over time. Inadequate upkeep can compromise the integrity of the equipment, increasing the risk of exposure to hazards and reducing the level of safety for workers. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to maintain and care for PPE to guarantee its longevity and continued effectiveness:
Regular Inspection
PPE should be inspected routinely before each use to check for any signs of wear, damage, or deterioration. For example, helmets should be examined for cracks or dents, gloves for tears or punctures, and respirators for proper seals and intact straps. If any part of the PPE is damaged or compromised, it must be repaired or replaced immediately. Workers should be trained to identify potential defects and know the critical areas to inspect, ensuring that no defective PPE is used, which could lead to preventable injuries.
Cleaning and Sanitization
Keeping PPE clean is essential to maintain its protective qualities and prevent contamination, especially in environments where chemical, biological, or particulate hazards are present. Items like respirators, goggles, and protective clothing should be cleaned according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For instance, respirators may require gentle washing with a mild detergent, while safety goggles need to be wiped with a disinfectant to remove dust or harmful particles. Regular sanitization is especially important in healthcare and laboratory settings to prevent the spread of infections. Additionally, certain types of PPE, like disposable gloves, should not be reused and must be properly disposed of after a single use to maintain hygiene standards.
Proper Storage
Storing PPE correctly is essential to protect it from environmental factors that could degrade its materials, such as direct sunlight, moisture, or extreme temperatures. Helmets, for example, should be stored in a cool, dry place away from sunlight, which can weaken the plastic. Respiratory masks should be kept in airtight containers to prevent contamination and maintain their filtration efficiency. Ensuring that PPE is stored neatly and securely also helps prevent it from becoming damaged or contaminated between uses.
Following Manufacturer Guidelines
Each piece of PPE comes with specific maintenance requirements set by the manufacturer. These guidelines detail how to clean, disinfect, and store the equipment properly, as well as any limitations on the number of uses or lifespan of the product. Adhering to these instructions is crucial for ensuring PPE effectiveness. For instance, flame-resistant clothing may require special laundering techniques to preserve its protective qualities, and hearing protection devices might have recommended intervals for replacing foam inserts or seals.
Scheduled Maintenance and Professional Servicing
Some PPE, particularly complex equipment like respirators or fall protection harnesses, may require scheduled maintenance or professional servicing. Employers should establish a maintenance schedule to track and record when PPE was last checked, serviced, or replaced. Professional servicing can include testing the integrity of protective gear or recalibrating equipment to ensure compliance with safety standards. Keeping a maintenance log helps track the condition of PPE and ensures it remains in optimal working order.
Employee Training on PPE Care
Proper PPE maintenance starts with comprehensive training for employees. Workers must understand the importance of caring for their equipment and be equipped with the knowledge to do so effectively. Training should cover how to inspect PPE for defects, the correct cleaning methods, and the protocols for reporting damaged or faulty equipment. Ongoing education and reminders can reinforce these practices and encourage a culture of safety and responsibility.
By implementing diligent maintenance and care practices, organizations can ensure their PPE continues to provide the necessary level of protection, reduce the need for frequent replacements, and contribute to a safer work environment for all employees.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Chapter 7
What Are Key Considerations for Buying Personal Protective Equipment(PPE)
Choosing the appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a critical step in ensuring the safety and well-being of workers in hazardous environments. The effectiveness of PPE depends not only on selecting the right type for each specific risk but also on how well it is maintained and used. Here is an expanded look at the essential factors to consider when choosing PPE:
Risk Assessment
The foundation of any PPE selection process is a comprehensive risk assessment. This involves carefully identifying and evaluating all potential hazards present in the workplace, such as chemical exposures, electrical dangers, sharp objects, or airborne contaminants. Understanding the nature, severity, and frequency of these risks allows for the selection of PPE that is specifically designed to mitigate them. For example, in a chemical plant, a risk assessment might reveal the need for chemical-resistant gloves, splash-proof goggles, and full-body suits, while a construction site might prioritize hard hats, steel-toe boots, and high-visibility vests. Tailoring PPE to these identified risks ensures that workers are adequately protected from the unique threats they face in their daily tasks.
Fit and Comfort
Proper fit and comfort are crucial to the effectiveness of PPE. Ill-fitting equipment, whether too loose or too tight, can compromise protection and make it difficult for workers to perform their tasks efficiently. For instance, loose gloves can get caught in machinery, while tight respirators may cause discomfort and lead to improper sealing. Furthermore, uncomfortable PPE is likely to discourage consistent use, increasing the risk of exposure to hazards. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that PPE is properly sized and adjusted for each worker. This may involve providing multiple sizes and conducting fit tests, especially for items like respirators, to confirm that they provide a secure and comfortable seal. The goal is to strike a balance between maximum protection and ease of use, encouraging workers to wear their PPE without reluctance.
Compliance Standards
PPE must meet established industry safety standards and regulatory requirements to ensure it provides reliable protection. Compliance standards are set by organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and other international regulatory bodies. These standards outline the minimum performance criteria that PPE must meet, covering aspects such as impact resistance, chemical permeability, and flame retardancy. Employers should always verify that the PPE they procure is certified and tested to these standards. Additionally, staying informed about updates to regulations and emerging safety technologies is essential to maintain compliance and provide the highest level of protection for workers. Selecting PPE that meets or exceeds these standards not only ensures safety but also protects the organization from potential legal and regulatory consequences.
Durability and Maintenance
The durability of PPE is another important consideration, particularly in environments where equipment is exposed to harsh conditions, such as high temperatures, corrosive substances, or rough physical activity. PPE must be robust enough to withstand the stresses of the work environment without degrading or losing effectiveness. For example, fire-resistant clothing worn by firefighters must endure repeated exposure to flames and heat without deteriorating. However, even the most durable PPE requires regular maintenance and inspection to ensure ongoing protection. This includes checking for wear and tear, cleaning equipment according to manufacturer guidelines, and promptly replacing any items that show signs of damage. Establishing a maintenance schedule and training workers to recognize when PPE needs to be serviced or replaced are critical steps in sustaining its protective capabilities.
Training
Proper training is essential to maximize the effectiveness of PPE. Workers must be educated on how to correctly wear, use, and care for their equipment. This includes understanding how to adjust PPE for a secure fit, recognizing the limitations of their protective gear, and knowing when to replace or clean it. Training should also cover emergency procedures in case PPE fails or needs to be removed quickly. Moreover, employees should be made aware of the reasons behind using specific PPE, emphasizing the potential hazards they are protecting against. A well-informed workforce is more likely to use PPE consistently and correctly, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Regular refresher training sessions and practical demonstrations can help reinforce this knowledge, ensuring that safety practices remain top-of-mind for all workers.
By carefully considering these factors—risk assessment, fit and comfort, compliance standards, durability and maintenance, and training—organizations can create a comprehensive PPE strategy that effectively safeguards their workforce and promotes a culture of safety.
Chapter 8
What to Look for in a Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) Supplier / Manufacturer
Selecting a reliable PPE supplier is crucial for worker safety and operational efficiency. Here are the key considerations:
Compliance and Certification: Ensure the supplier’s products meet safety standards such as ANSI, OSHA, or ISO. Certifications guarantee that PPE is rigorously tested and reliable.
Product Range and Customization: Choose a supplier that offers a wide variety of PPE for different risks and provides customization options to suit your unique requirements.
Quality and Durability: Assess the materials and durability of the PPE, especially for demanding environments. Conduct trials or check reviews for real-world performance.
Reputation and Experience: Opt for well-established suppliers with positive industry feedback. Their experience often translates to higher reliability and expertise.
Customer Service: A responsive and supportive supplier can address urgent needs and provide technical guidance, enhancing your overall safety strategy.
Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier has a stable supply chain and the capacity to handle large or urgent orders without delays.
Innovation: Consider suppliers investing in advanced safety technology, offering up-to-date, effective solutions like smart PPE or ergonomic designs.
Sustainability: Look for suppliers committed to ethical and eco-friendly practices, which can align with your company’s sustainability goals.
Cost and Value: Balance cost with product quality and service. Higher-quality PPE may have better durability and long-term cost-effectiveness.
Training and Support: A good supplier provides resources and training to ensure proper PPE use, enhancing worker safety and compliance.
By prioritizing these factors, you can select a PPE supplier that meets your safety requirements and acts as a reliable partner.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
In Summary
In Summary
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for protecting workers from a wide range of hazards across various industries, including construction, healthcare, and chemical processing. It acts as a critical barrier, ensuring safety from physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic risks. PPE is categorized into types such as head protection, eye and face shields, hearing protection, respiratory masks, gloves, body suits, and safety footwear, each designed for specific threats.
Conducting a proper PPE risk assessment is key to selecting suitable protective gear. This involves identifying workplace hazards, analyzing risks, and determining the necessary PPE. Factors like fit, comfort, durability, and compliance with standards (e.g., ANSI, OSHA) must be considered. Effective PPE use also requires regular maintenance and comprehensive training to ensure workers understand how to use and care for their equipment properly.
PPE regulations enforce compliance to maintain safety standards, and in emergencies, such as chemical spills or health crises, PPE becomes even more vital. Innovations, such as smart PPE and advanced materials, continue to improve safety and comfort. Despite challenges like discomfort or supply issues, PPE remains a cornerstone of workplace safety, with ongoing advancements crucial for future protection.
CONTACT US
- Feel free to contact us any time. We will get back to you as soon as we can!
Get in Touch
- +86-17330061805
Address
- No.7 Building, No.63, Jianda Road, Huojiatun Village, Loudi Town, Luancheng District, Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province, China